Install git
Before starting this tutorial, you have to check the git is installed on the system or not. Git is not installed by default on Ubuntu operating system. Run the following command to install git on Ubuntu.

Install Fugitive Plugin
Run the following command to install the fugitive plugin on Ubuntu.

Initialize git repository
It is necessary to initialize git repository before executing any git command. ‘git init’ command is used to initialize a git repository for any existing or new project. Run the following command from the terminal to initialize an empty git repository.

Adding file in git repository
A text file named employee.txt is used to test the uses of the fugitive plugin in this tutorial. The content of this file is given below.
employee.txt
11002 HR 32 $1500
11003 Marketing 26 $1200
11004 HR 25 $2500
11005 Sales 30 $1000
‘git add <file>’ command is used to add modification in the current working directory and add the file in vim buffer. It informs git command to add the update in a particular file after running ‘git commit’ command.

The command, ‘git commit’ will require to run for saving the updates of any file in the local repository. Run the command from the terminal.
Remove the ‘#’ symbol from the line, ‘modified: employee.txt’ file to save the changes of this file.

Using Gblame
‘git blame’ command is used to show the details of the most recent modification of any file for each line. Run the command from the terminal for the file, employee.txt.
It will show a similar output like the following image.

You can get the same output of the above command from vim editor by using ‘:Gblame’ wrapper of fugitive plugin. You don’t need to the terminal the editor to do the task. Open, ‘employee.txt’ file in the vim editor by running the following command.
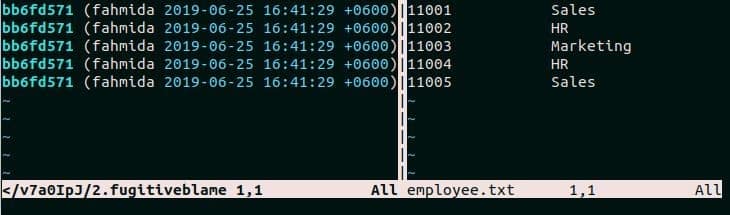
Press ESC and :Gblame to retrieve the recent modification information of the file in the editor.
: Gblame
You will get the following formatted output after pressing Enter key.
‘:Gdiff’ wrapper is used as the alternative of ‘git diff’ command. When it used for any particular file then it displays the difference between the previous content and present content of the file after current commit. ‘:Gdiff’ can be used to display the difference between any revision of the file. It can take an argument of any revision to retrieve the particular version of the file. There are two other related commands for searching the difference between any two versions of the file by adding or retrieving any diff section. These commands are ‘:diffput’ and ‘:diffget’. The use of ‘:Gdiff’ command is shown in the next section of this tutorial.
Open employee.txt file and press ‘i’ to enable the INSERT mode. Modify the file by adding an entry for the employee, ‘11006’. Press ‘ESC’ and ‘:x’ to save and close the file.
Re-open the file, employee.txt in the vim editor and type ‘:Gdiff’ and press Enter to find out the difference between the current commit and the previous version of the file.
: Gdiff
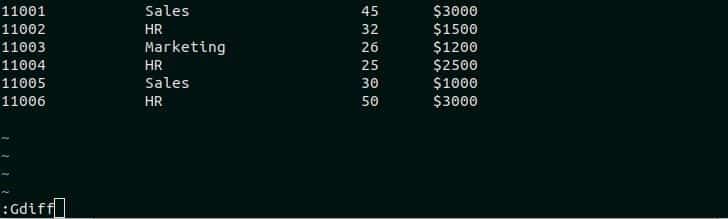
The following output will display after executing the ‘:Gdiff’ command. The newly inserted record will be displayed as highlighted text to show the difference.

‘:Gread’ command works as the alternative of ‘git checkout <file>’ command. It can also take the argument of any revision file like ‘:Gdiff’ command.
: Gread
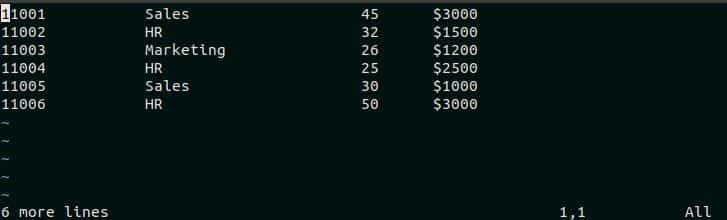
When this command is executed for the current version of the employee.txt file then it will show the following output. The file contains 6 employee records and the output shows the text ‘6 more lines’.
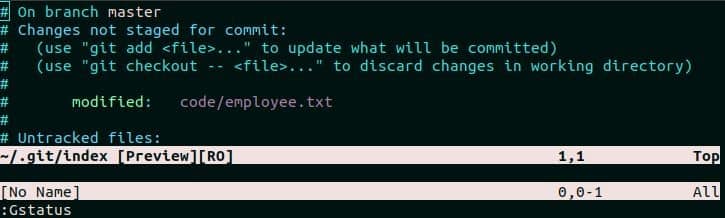
‘:Gstatus‘ command works as the alternative of ‘git status’ command. It shows detail information about the status of all files or the current file. There are many custom key to interact with the status window. Some of them are D, cc, <C-p>, <C-n> etc. Open employee.txt file in the vim editor and run ‘:Gstatus’ command.
: Gstatus
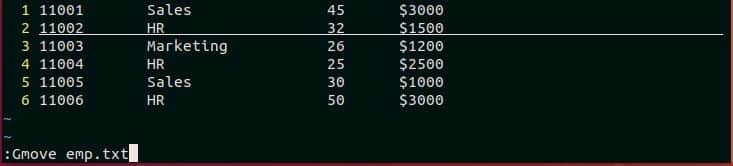
‘:Gmove’ command works similar to ‘git mv’ command. It is used to rename any existing file from vim editor. Suppose, you want to rename employee.txt file by emp.txt. Open the file in vim editor and type the following command and press Enter to rename the file.
:Gmove emp.txt
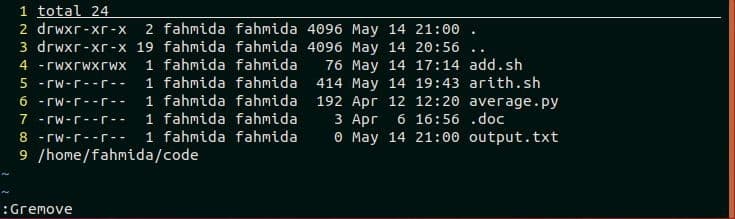
‘:Gremove’ command works similar to ‘git rm’ command. It is used to delete the file from the vim buffer and current working directory. Open the file that you want to delete from the current working directory and run the command with ‘!’ symbol to forcefully delete the file. Here, employee.txt file is selected for deletion.
:Gremove!
Conclusion
How the vim users can execute git commands by using vim plugin is shown in this tutorial. If you need to execute git commands and want to use vim editor together then it is better to use fugitive plugin of vim. Hope, after reading this tutorial the reader will be able to use fugitive plugin and run basic git commands from vim editor.




