Boot Repair is a tool to repair common boot issues on Ubuntu, Debian, Arch, Linux Mint, OpenSUSE, Fedora and other Linux distributions, Windows and Mac OS operating systems.
If you install Windows operating system after you’ve installed a Linux distribution such as Ubuntu, you won’t be able to boot into your Linux operating system. Boot Repair can help.
Anything can go wrong while multi-booting Linux operating systems. Boot Repair can help as well.
Boot Repair can
- Backup partition table
- Backup device boot sectors
- Install GRUB bootloader
- Configure GRUB bootloader
- Add kernel options
- Change the default OS in GRUB
- Restore a Windows compatible MBR
- Repair a broken filesystem
- And many more.
You can learn more about Boot Repair at https://sourceforge.net/p/boot-repair/home, the official website of Boot Repair.
In this article, I will show you how to use Boot Repair on Ubuntu. I will be using Ubuntu 18.04 LTS for the demonstration. Let’s get started.
Installing Boot Repair:
You usually install Boot Repair on an Ubuntu live boot as you may not be able to boot into your operating system installed on the hard drive at that time. So this is what I am going to focus on in this article.
You can make an Ubuntu bootable USB stick of any latest version of Ubuntu Live DVD ISO image. I have a dedicated article on that topic, which you can read at https://linuxhint.com/rufus_bootable_usb_install_ubuntu_18-04_lts/
Once you’re done with making a bootable USB stick of Ubuntu Live DVD ISO image of your choice, boot from it and select Try Ubuntu without installing from the GRUB menu as shown in the screenshot below.

Now connect to your network and open a Terminal window (Press <Ctrl> + <Alt> + t)
Boot Repair is not available in the official package repository of Ubuntu. So you have to install it from the Boot Repair PPA.
Now add the PPA of Boot Repair with the following command:

Now press <Enter> to continue.
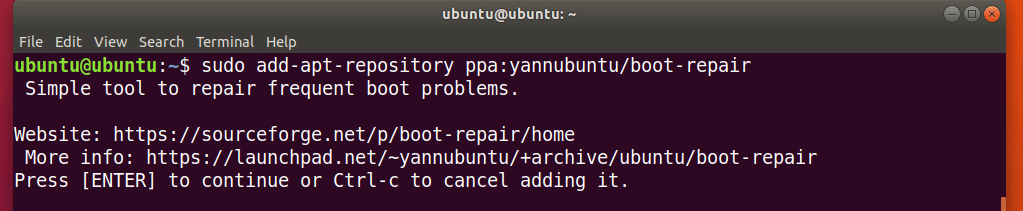
The Boot Repair PPA should be added and the APT package repository cache should be updated.
Now you can install Boot Repair with the following command:

Now press y and then press <Enter> to continue.

Boot Repair should be installed.
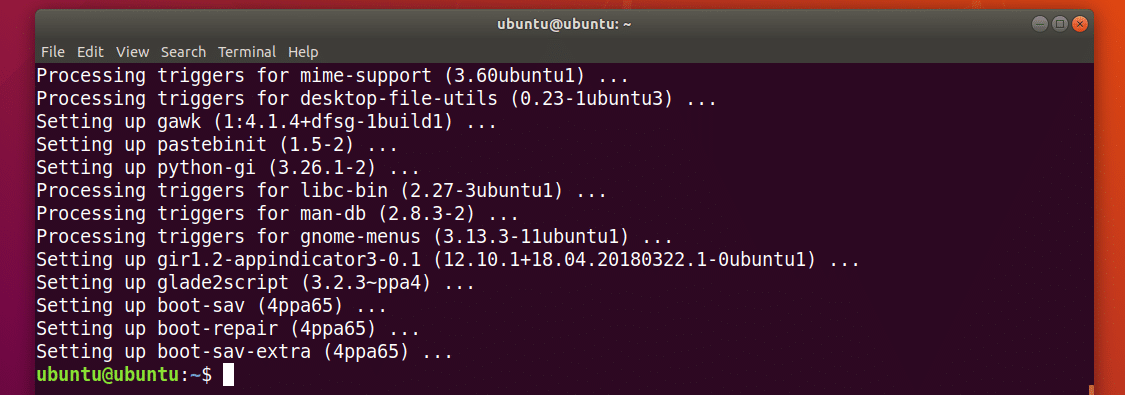
Now you can start Boot Repair Application Menu:
You can also start Boot Repair from the command line with the following command:

Boot Repair should start.
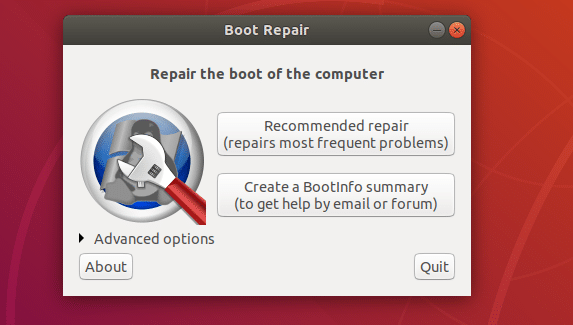
Repair Boot Problems with Boot Repair:
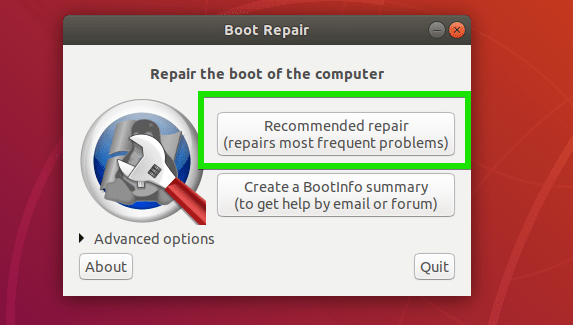
The most common repair option of Boot Repair is Recommended repair as marked in the screenshot below. It should repair most of the boot issues you may face.
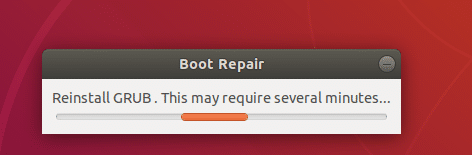
Once you click on it, it should find and fix boot problems for you.
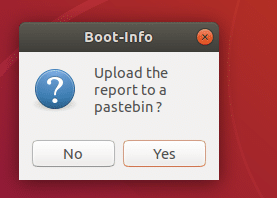
you will see the following option. You can upload the report to pastebin by clicking on Yes. If you don’t want that, just click on No.
The repair process should continue.

Once the repair is complete, you should see the following window. Just click on OK.
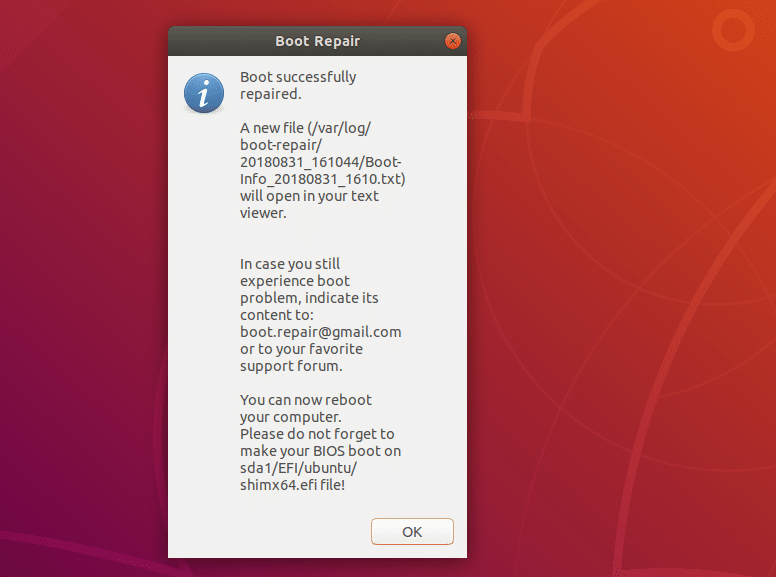
A text document should also open up. It contains information about your entire system and what Boot Repair did to it in order to repair boot problems.

Now you should be able to boot into your installed operating systems as usual.
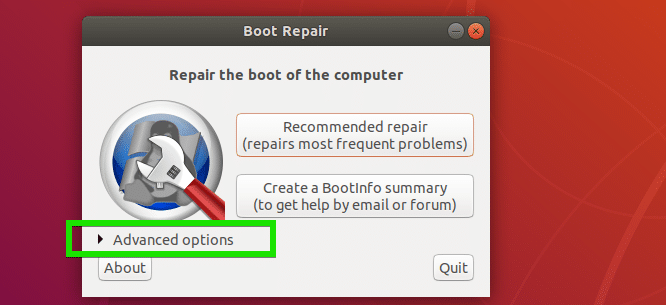
There are many advanced repair options in Boot Repair. Just open Boot Repair and click on Advanced Options as marked in the screenshot below to reveal them.
As you can see, there are many advanced options in Boot Repair.
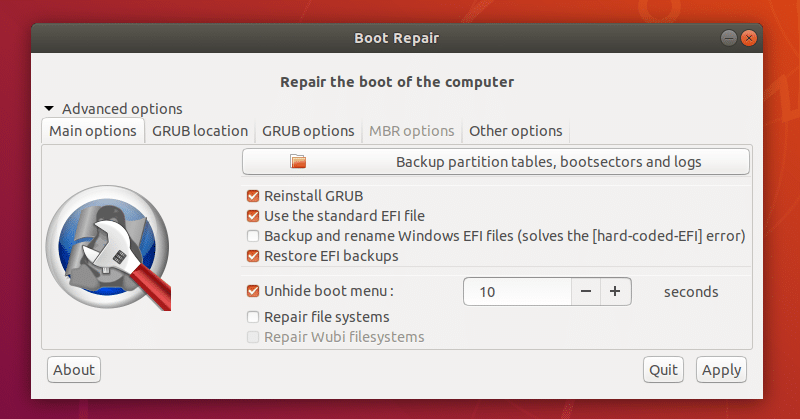
I will talk about these in the next sections of this article below.
Backing Up Partition Table with Boot Repair:
You can backup your partition table from Boot Repair. It is important as if your partition table gets corrupted somehow, you will be able to recover the partitions and get your data back. Otherwise, you may loose all your data.
To backup your partition tables, just click on Backup partition tables, bootsectors and logs button as marked in the screenshot below.
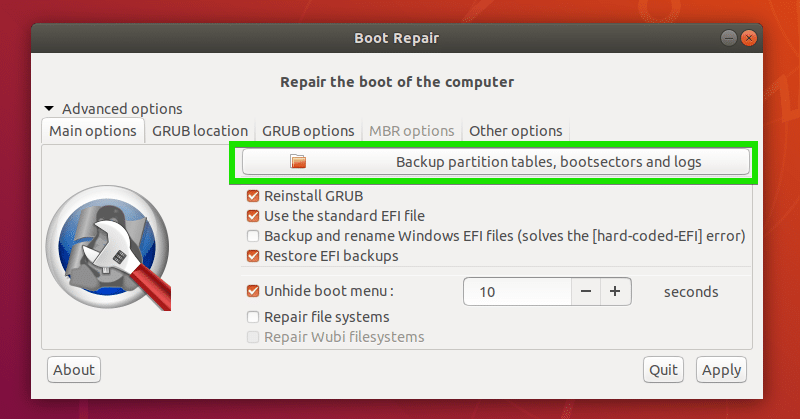
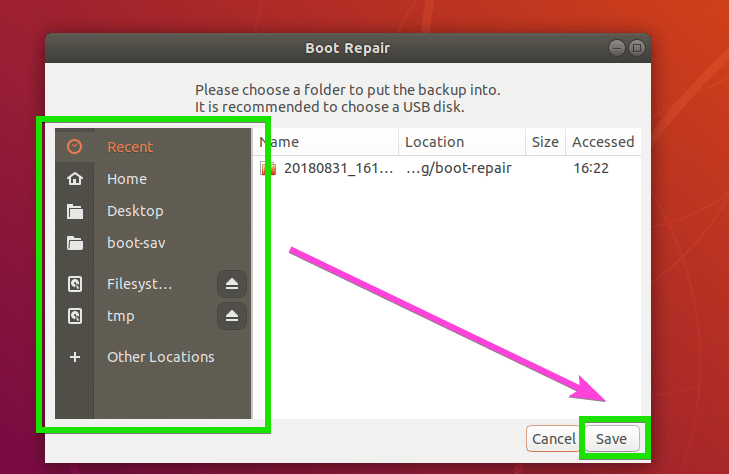
Now select a location where you want to save the partition table data and click on Save.
Saving partition table….
Once the partition table is saved, you should see the following message. Just click on OK.

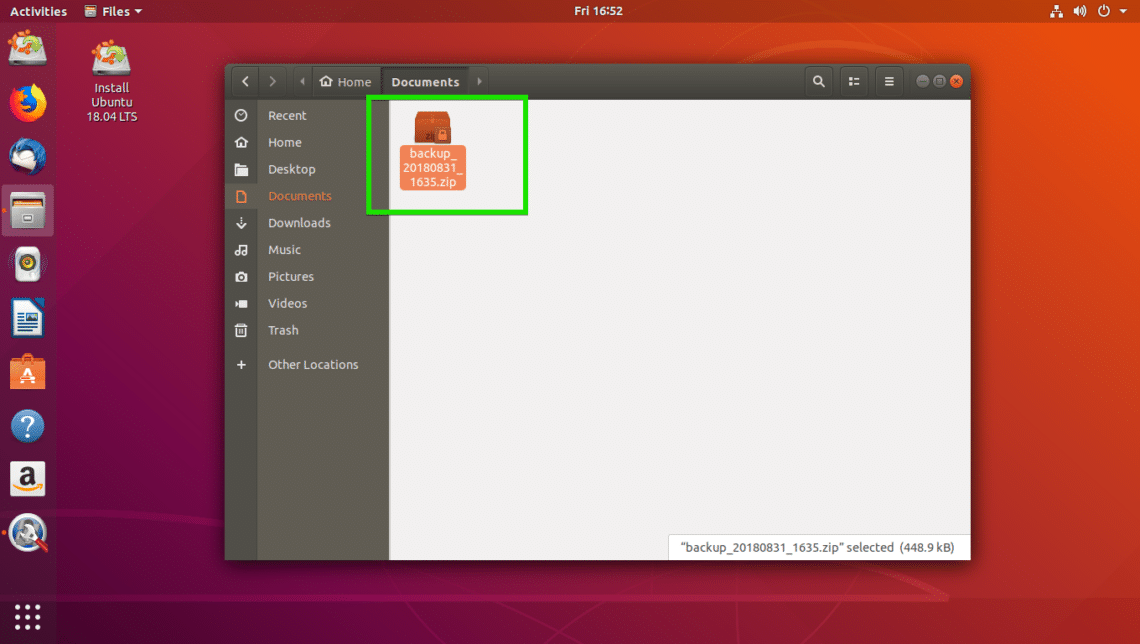
Now you should be able to find a zip file in the directory that you selected earlier as you can see in the screenshot below.
Repairing File Systems with Boot Repair:
At times, your file systems may get corrupted and Ubuntu won’t be able to fix it automatically on boot. It may result in boot failure. You can fix the file system with Boot Repair. Just check the Repair file systems option from the Main options tab as marked in the screenshot below and click on Apply.
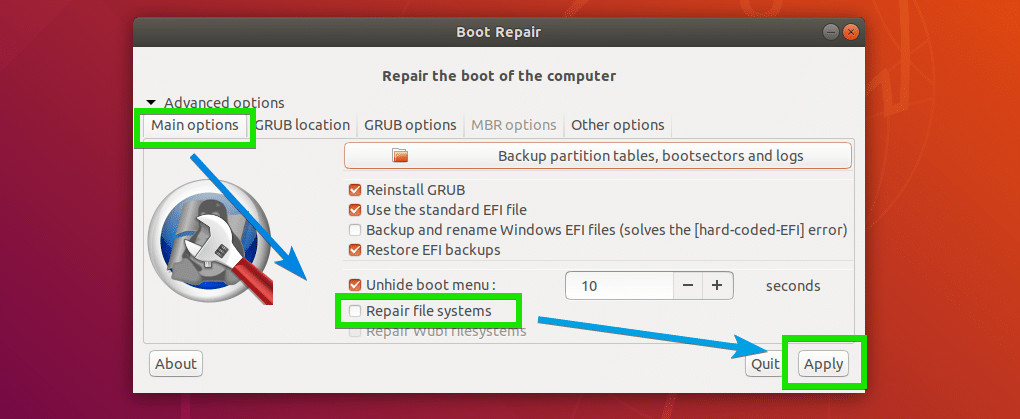
It should take a while to repair the filesystem and fix boot problems. Once it’s done, you should be able to boot into your installed operating systems as usual again.
Changing GRUB Location with Boot Repair:
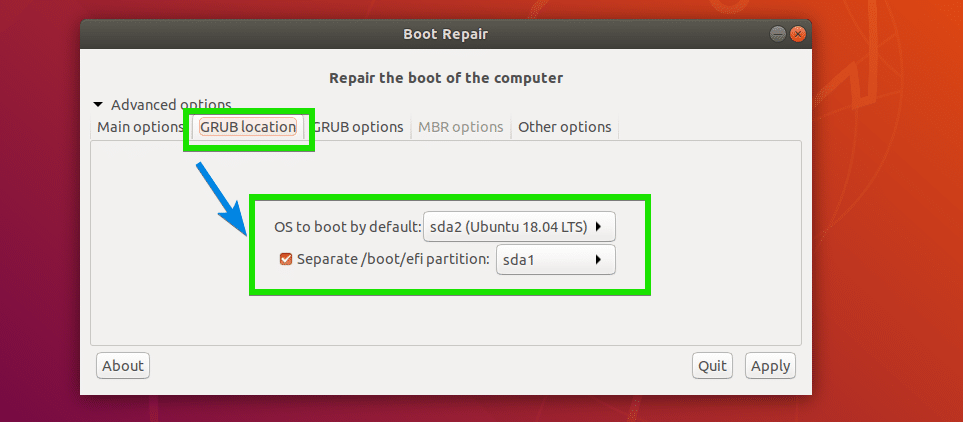
You can tell where GRUB is installed on your hard drive from the advanced options of Boot Repair. If you have multiple hard drives installed on your computer that has GRUB installed, then you may want to set which hard drives you want to repair here.
To change GRUB location, go to the GRUB location tab of Boot Repair. Now select the hard drive partition from the OS to boot by default drop down menu. If you’re using UEFI based motherboard, then also select the hard drive partition which is used as EFI System Partition from Separate /boot/efi partition drop down menu.
Changing GRUB Options from Boot Repair:
You can also change many of the GRUB options from the GRUB options tab of Boot Repair as you can see in the screenshot below.

That’s basically how you install and use Boot Repair on an Ubuntu Live System. Thanks for reading this article.