Services on Linux Debian 10 Buster
A service is a program running on the background to be used when needed. Apache, ssh, Nginx or Mysql are some of the most known services. On Debian, including Debian 10 Buster, services are stored in the directory /etc/init.d/, they can be managed with the init system or the systemd, both of which will be explained below with examples of 3 different ways to stop, start, restart or check a service status.
- The service command
- Systemd
- The /etc/init.d directory
- Checking a service status on Linux Debian 10 Buster
- Starting services on Debian Linux 10 Buster
- Stopping services on Linux Debian 10 Buster
- Restarting services on Linux Debian 10 Buster
- Related articles
The service command
The command service in Linux allows to check the status, stop, start or restart services and daemons, init files stored under the /etc/init.d directory.
The syntax to stop, run, restart services or print their status at demand is:
The following example shows how to check the ssh service status using the service command:
Systemd
The Systemd is a suite to manage Linux services and daemons (the last “d” is because of Unix daemons). The systemctl command allows to start,stop,restart and check services status. Its aim is to unify the configuration and behaviour for all Linux distributions replacing Unix SystemV and BSD init systems.It also manages the init program described below.
The syntax to check the status of a service is the following:
The /etc/init.d directory
When the system boots init is the first program to be executed and remains running as process with PID 1 until the system turns off.“ It is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes and automatically adopts all orphaned processes. Init is started by the kernel during the booting process; a kernel panic will occur if the kernel is unable to start it. Init is typically assigned process identifier 1” (Source: Wikipedia)
All services and daemons starting at boot are found in the /etc/init.d directory. All files stored in the /etc/init.d directory support stopping, starting, restarting and checking services status.
The syntax to check the status of the ssh service is:
Checking a service status on Linux Debian 10 Buster
Below you’ll find 3 different ways showing how to check for a service status on Debian 10 Buster (or any modern Debian release).
Checking a service status with the command service:
The command service allows to show a service status, to start, stop or restart it, to show a service the syntax is:
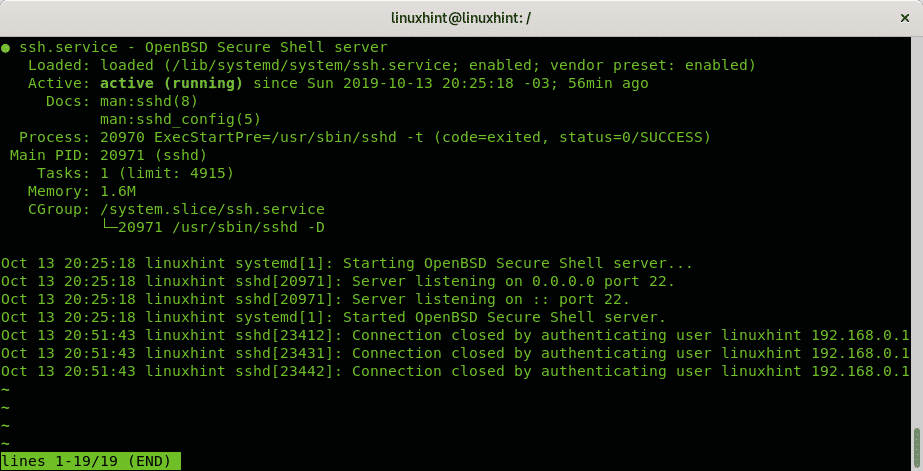
The following example shows the ssh service status:
In my case in which the ssh service is running the output is:
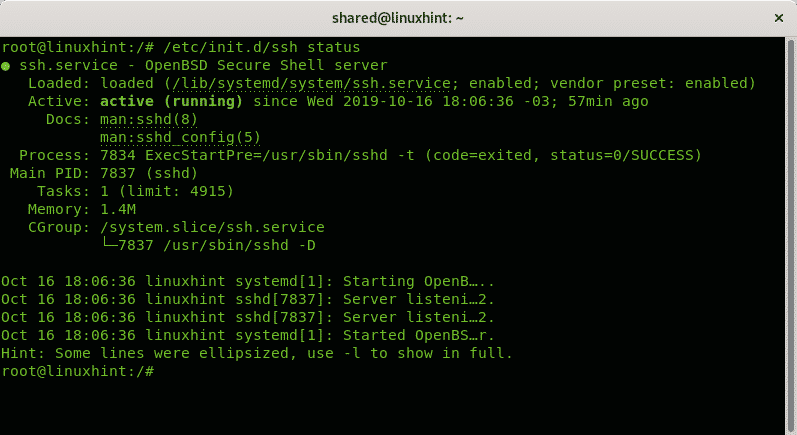
Checking status of services within init.d:
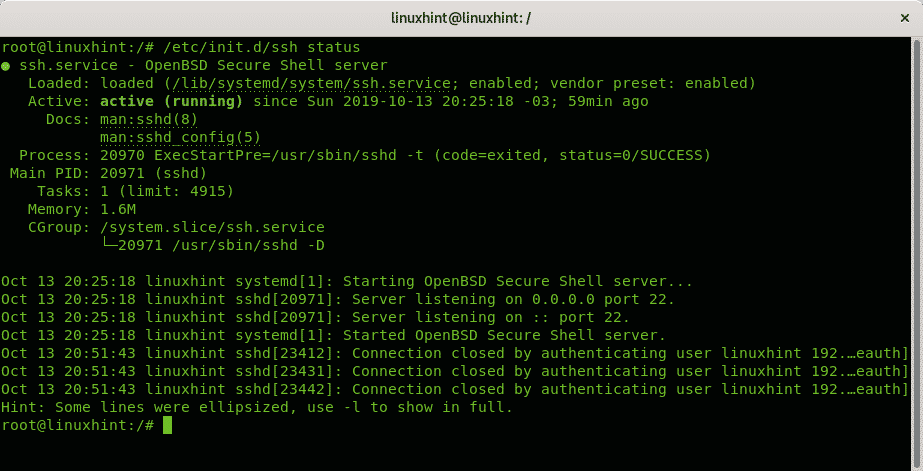
Additionally to the command service you can also interact with services stored at the /etc/init.d directory, to check a service status the syntax is:
To check the status of the ssh service run:
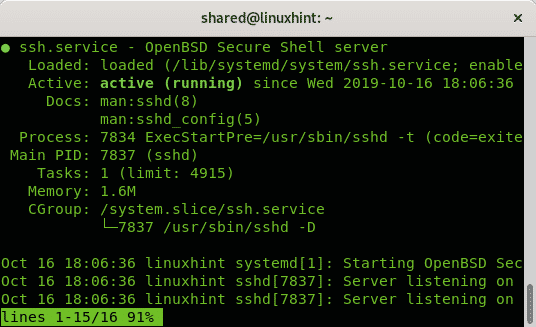
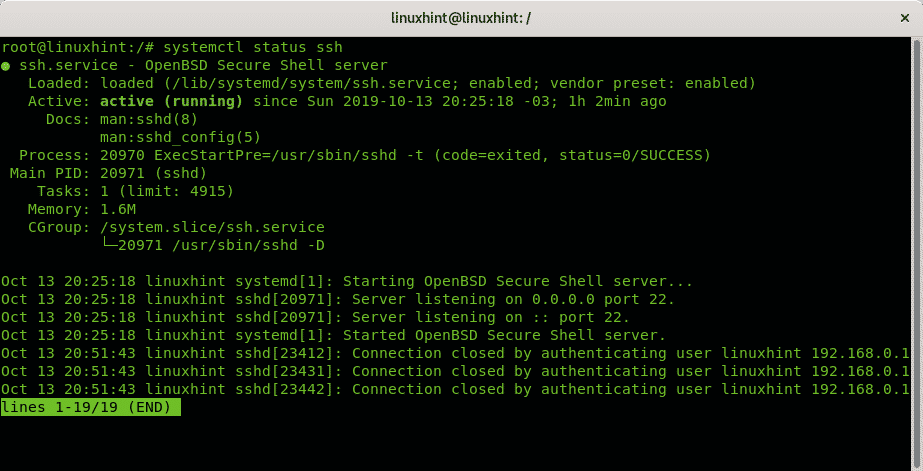
And you can also check a service status using the Systemd control command systemctl, the syntax is:
To check the ssh status using the systemctl command run:
Starting services on Linux Debian 10 Buster
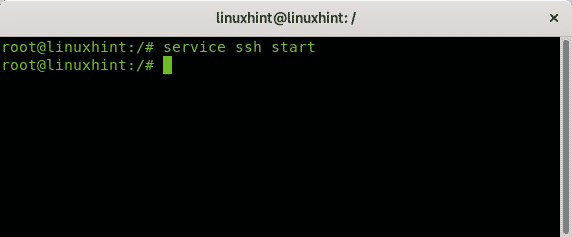
To start services on Linux using the command service the syntax is:
The following example shows how to start the ssh service using the service command:
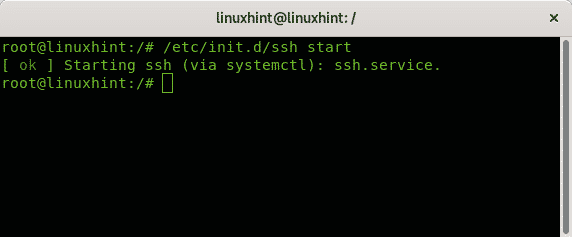
Like with the status you can also start services from the init.d directory getting an informative output, the syntax is:
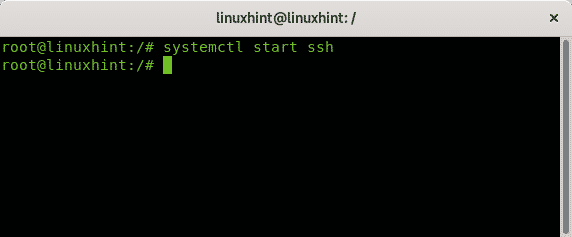
You can also start services using the systemctl command with the following syntax:
The following example shows how to start the ssh service using the systemctl command:
Stopping services on Linux Debian 10 Buster
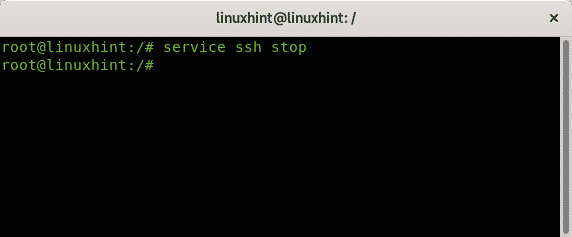
To stop services on Debian using the service command the syntax is:
The following example shows how to stop the ssh service:
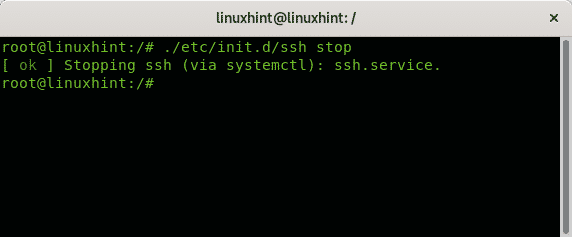
To stop services using the init.d directory the syntax is:
The example below shows how to stop the ssh service using the /etc/init.d directory:
To stop a service using the systemctl command the syntax is:
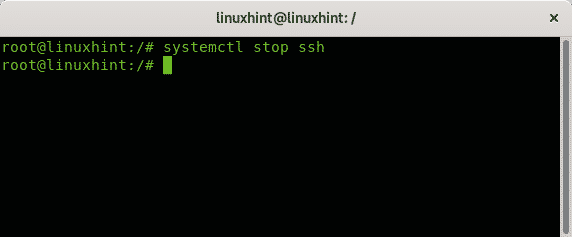
The example below shows how to stop the ssh service using the systemctl command:
Restarting services on Linux Debian 10 Buster
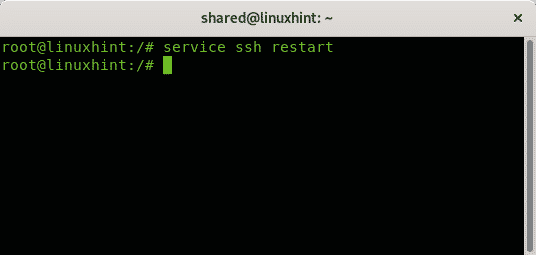
Restarting services requires the same syntax, to restart the ssh service using the command service run:
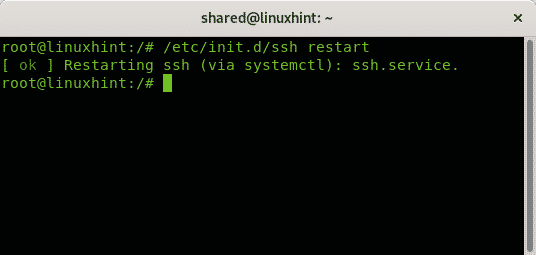
To restart the ssh service using the init.d directory run:
And finally to restart the ssh service using the Systemd run:
That’s all on managing services under Linux. Check the Related Articles section to learn more about services.
I hope you found this brief tutorial useful. Keep following LinuxHint for additional updates and tips on Linux and Networking.