Updating APT Package Repository Cache:
First, update the APT package repository cache with the following command:

The APT package repository cache should be updated.

Installing and Configuring MySQL/MariaDB:
Now, install MariaDB from the official package repository of Debian 10 with the following command:
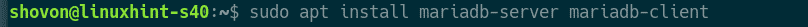
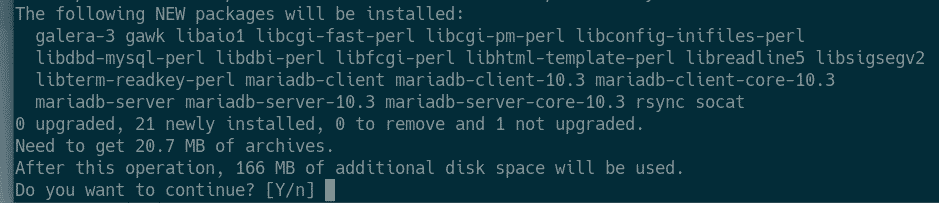
Now, press Y and then press <Enter> to confirm the installation.
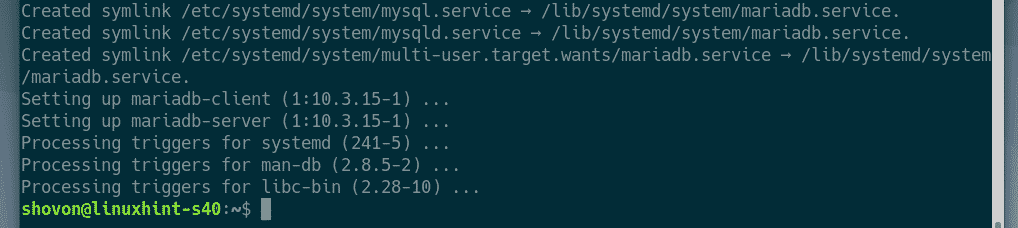
MariaDB should be installed.
Now, check whether mariadb service is running with the following command:

As you can see, mariadb service is running and it’s also enabled to start on system boot.

If the mariadb service is not running in any case, run the following command to start it.
Now, to set up a root password, run the following command:
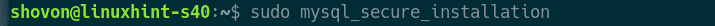
Now, press <Enter>.

Now, press Y and then press <Enter>.

Type in a new root password and press <Enter>.

Type in the root password again and press <Enter>.
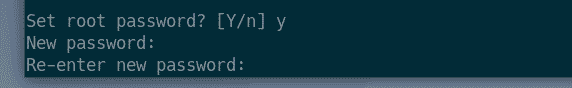
Press Y and then press <Enter> to remove anonymous users.
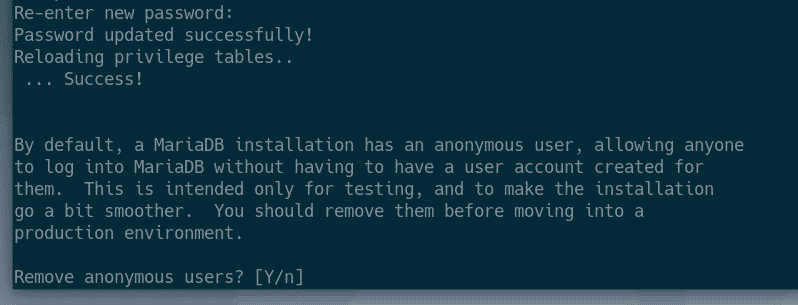
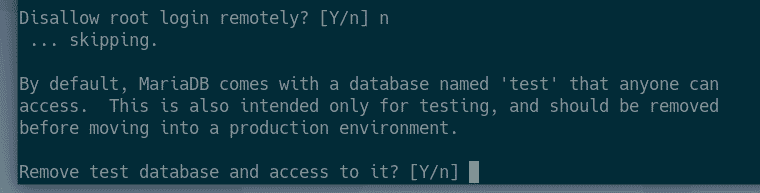
If you don’t want to allow root login remotely, press Y. Otherwise, press N. Then, press <Enter>.
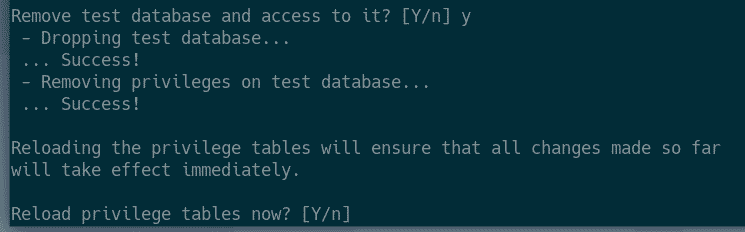
Now, press Y and press <Enter> to remove test database.
Now, press Y and then press <Enter> to reload the privilege table.
MariaDB should be configured.

Creating New MySQL/MariaDB Users and Databases:
Now, you have to create a new user and a database for your Laravel web application.
Login to the MariDB shell as root with the following command:

Now, type in the MariaDB root password that you’ve just set and press <Enter>.

You should be logged in.
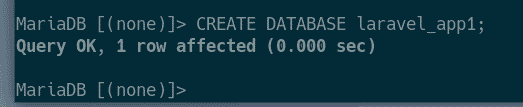
Now, create a database laravel_app1 with the following SQL statement:
Now, create a new user laravel, set a password for the user (let’s say 123) and grant the user permission to use the database laravel_app1 with the following SQL statement:
IDENTIFIED BY ‘123’;

Now, for the changes to take effect run the following SQL statement:
Now, exit out of the MariaDB shell as follows:
Installing PHP and Required PHP Libraries:
Now, install Apache 2 web server, PHP and all the required PHP libraries with the following command:
php-tokenizer php-xml php-zip

Now, press Y and then press <Enter> to confirm the installation.

Apache 2 web server, PHP and required PHP libraries should be installed.
Installing Composer:
Now, install Composer from the official Debian package repository with the following command:

Now, press Y and then press <Enter> to confirm the installation.
Composer should be installed.

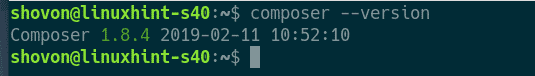
Now, run the following command check whether Composer is installed correctly.
Composer is working correctly.
Installing Laravel Installer with Composer:
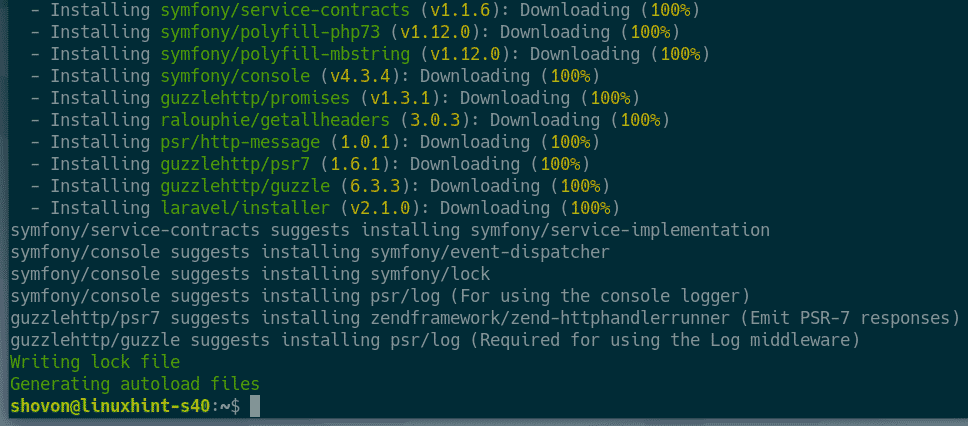
Now, install Laravel installer using Composer with the following command:

Laravel installer should be installed.
Now, add the composer binary path to the PATH environment variable with the following command:
~/.bashrc

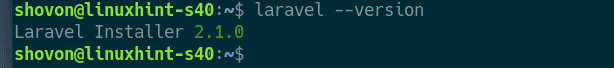
Now, close your Terminal and open a new one. Then, run the following command to check whether laravel command is accessible.
As you can see, the laravel command is working just fine.
Creating a Laravel Project:
First, navigate to your project directory as follows

Now, to create a new laravel project app1, run the following command
Laravel installer will download and install all the required files and packages. It will take a while to complete.
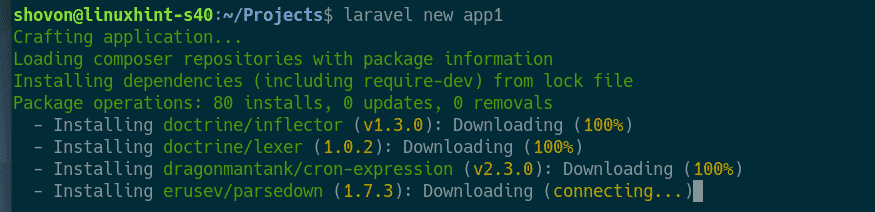
At this point, the project should be set up.

A new directory with the name of the project (app1 in this case) should be created as you can see in the screenshot below.
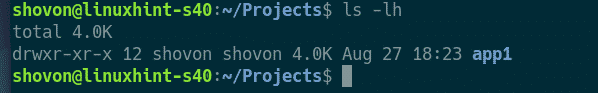
Navigate to the app1/ directory as follows:

The Laravel project files should be here.

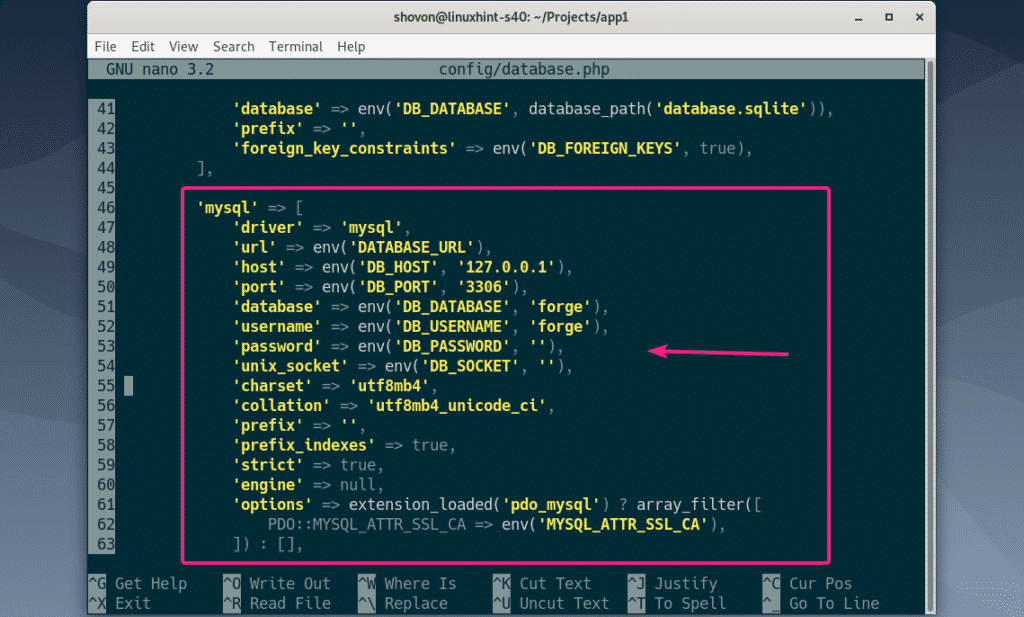
To configure Laravel to use the MariaDB database that we have created earlier, edit the config/database.php configuration file.

Now, find the mysql section as marked in the screenshot below.
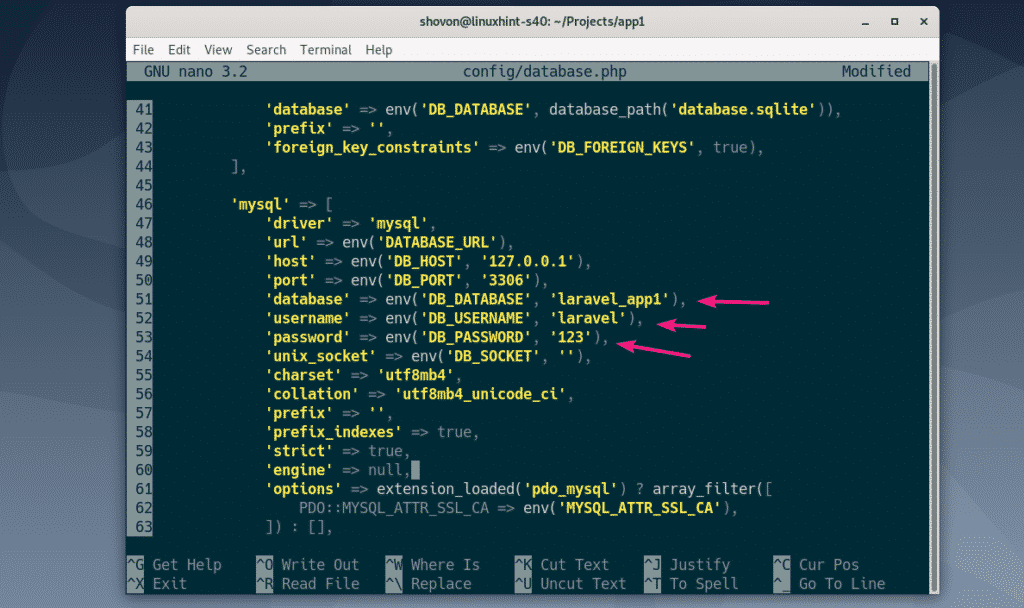
Now, change the database name, username and password fields as marked in the screenshot below. Once you’re done, save the file by pressing <Ctrl> + X followed by Y and <Enter>.
Now, start the PHP built in web server with the following command:

Now, the Laravel web app should be accessible on port 8000.
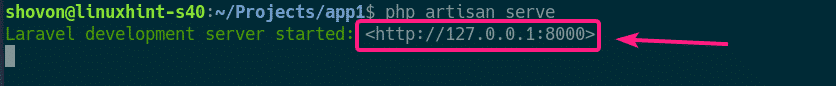
Now, open a browser and visit http://127.0.0.1:8000 or http://localhost:8000
You should see the default Laravel page as you can see in the screenshot below.
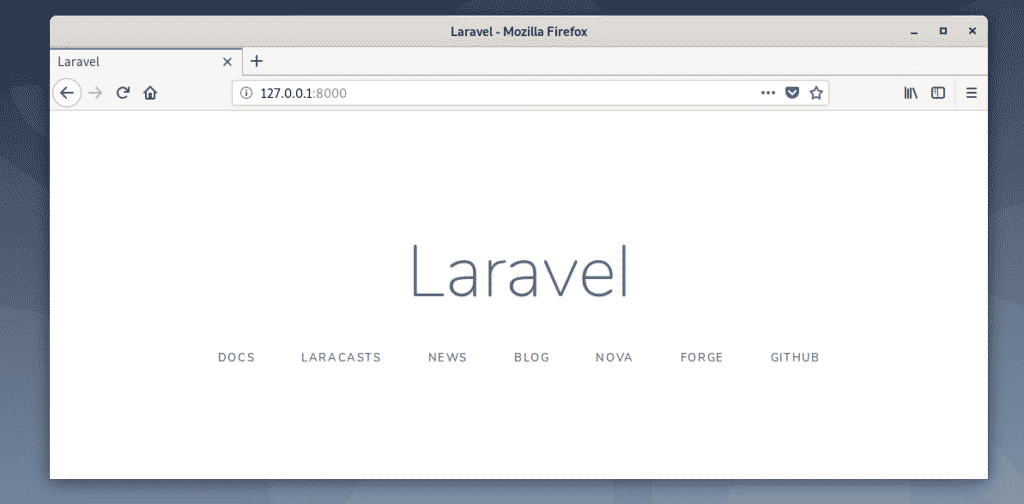
To learn more about Laravel, take a look at the official Laravel Documentation.
So, that’s how you set up a Laravel development environment on Debian 10 Buster. Thanks for reading this article.