In this lesson on Python sys module, we will study how this module allows us to interact with the interpreter and the host machine directly. Let’s see what all features this module offers to us.
Python sys module
The first advantage the sys module offers to us is its independence from the host machine Operating System. This means that this module can work the same even if it is working on Windows or Macintosh or Linux or any given OS. In this post, we will study the functions it provides to us. Let’s get started.
Working with sys module
To start working with the sys module and make scripts use this module, we will use the same import statement in all the scripts we write:
This statement imports and brings required sys module dependencies into our scope.
Python sys.argv
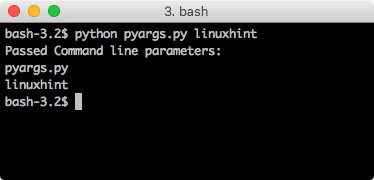
The most basic operation sys module allow us is to access the command line parameters passed to the script. Let’s write a program to demonstrate this:
print(‘Passed Command line parameters:’)
for param in sys.argv:
print(param)
When we run this program with command line parameters, we will see this output:
Note how this picked even the file name we passed to it as a command line parameter.
Python sys.path
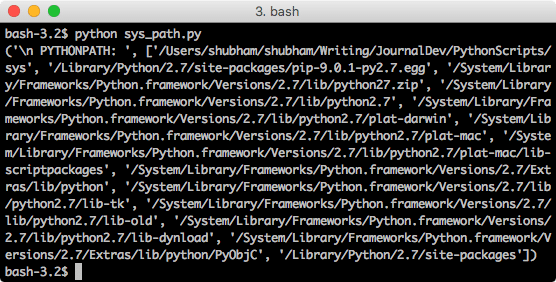
Using the path function, we can display the PYTHONPATH which is provided in the host machine. We will write a script to use this function now:
print(‘n PYTHONPATH: ‘, sys.path)
When we run this program, we will see this output:
Of course, this can vary based on your machine.
Python sys.stdin
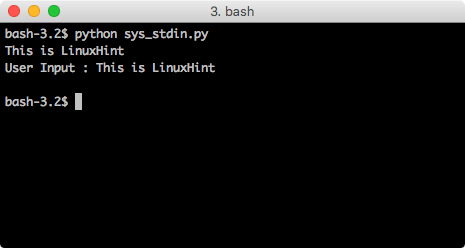
We can use the sys module to take input from the user as well. We will try this function now:
input_by_user = sys.stdin.readline()
print("User Input : " + input_by_user)
When we run this program, we will see this output:
This is very important function which we will usually use in our programs to take user input.
Python sys.copyright
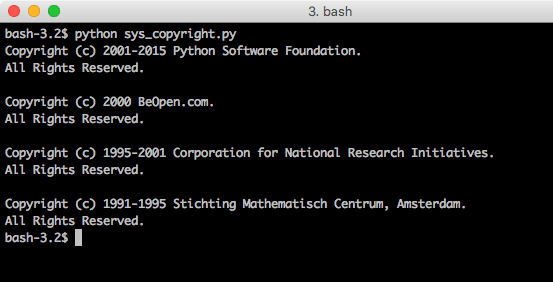
To display the copyright information related to currently installed Python version on the host machine, we can use this function:
print(sys.copyright)
When we run this program, we will see this output:
Python sys.exit
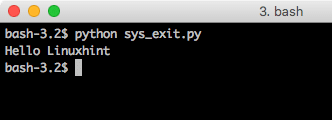
There are many use cases when we must choose to exit the program flow without doing anything else (like error handling etc.). This is easy to achieve using the exit function call:
print("Hello Linuxhint")
sys.exit(1)
print("Not printed!")
When we run this program, we will see this output:
In this quick post on Python, we saw how we can use various functions provided by sys module in Python and demonstrated them with example scripts. Go on and play with more of them.