Adding Zabbix Repository:
Zabbix is not available in the official package repository of CentOS 7. But, you can easily add the official Zabbix package repository on CentOS 7 and install Zabbix from there.
To install the official Zabbix package repository on CentOS 7, run the following command:
.noarch.rpm

The official Zabbix package repository should be installed.
Updating YUM Package Repository Cache:
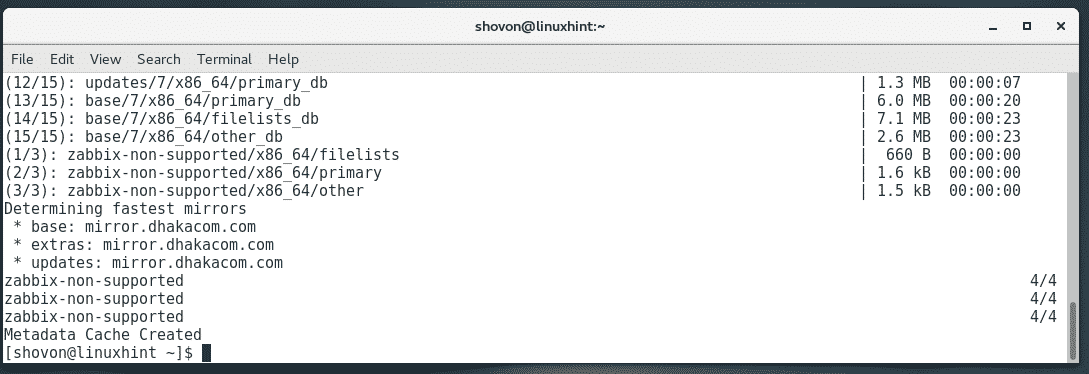
Now, run the following command to update the YUM package repository cache of your CentOS 7 machine:

The YUM package repository cache should be updated.
Installing Zabbix:
Now, you’re ready to install Zabbix and all the required packages on your CentOS 7 machine.
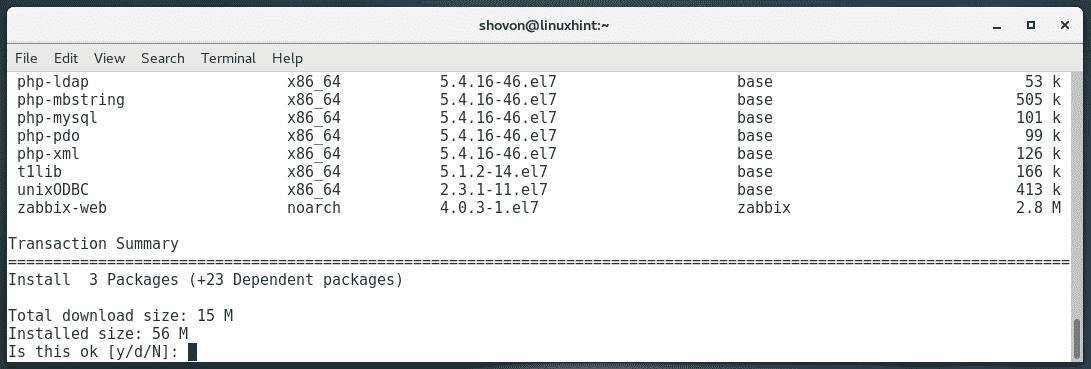
To install Zabbix on your CentOS 7 machine, run the following command:

Now, press y and then press <Enter>.
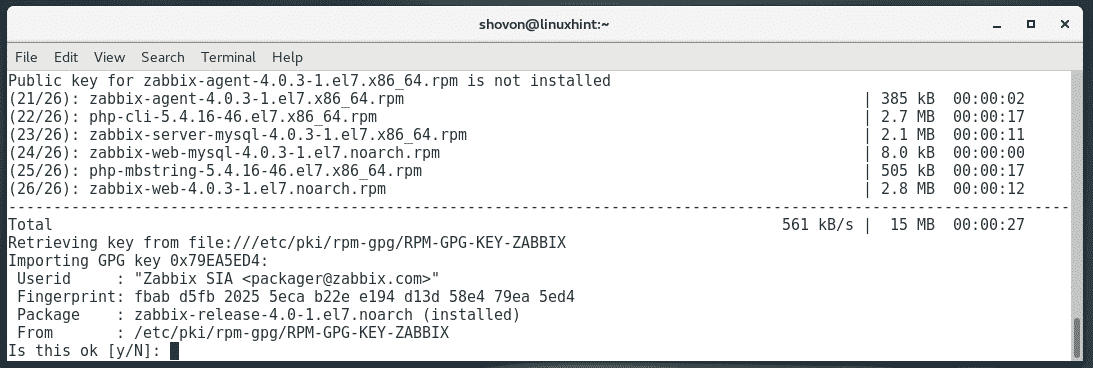
Zabbix packages are being downloaded.

Now, press y and then press <Enter> to accept the Zabbix GPG key.
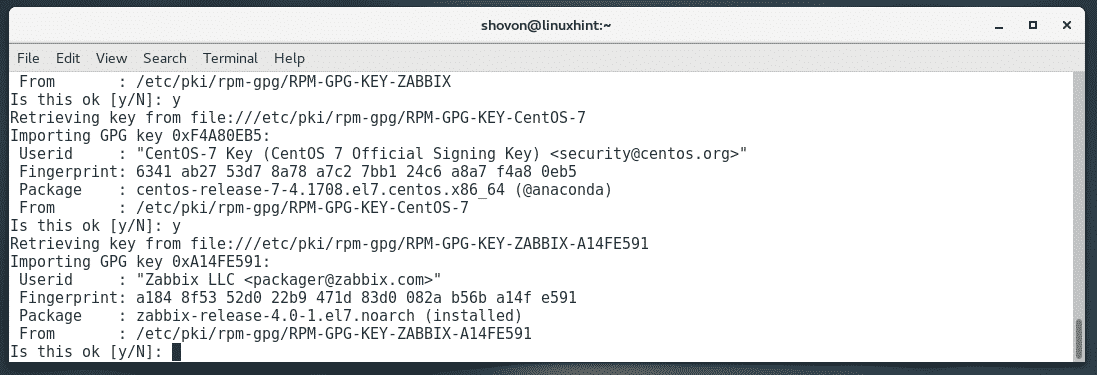
Now, press y and then press <Enter> to accept the CentOS 7 GPG key.

Now, press y and then press <Enter> to accept the Zabbix GPG key again.
Zabbix should be installed.
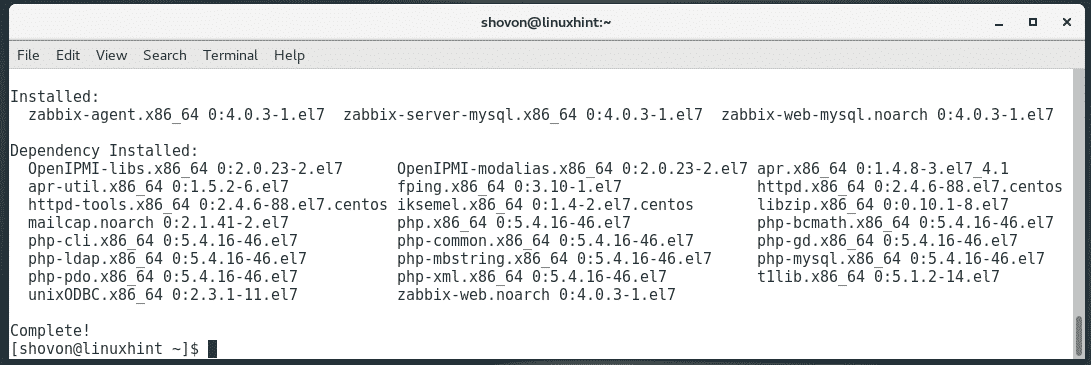
Installing MariaDB Database:
Now, you have to install MariaDB. MariaDB will be used as Zabbix datastore.
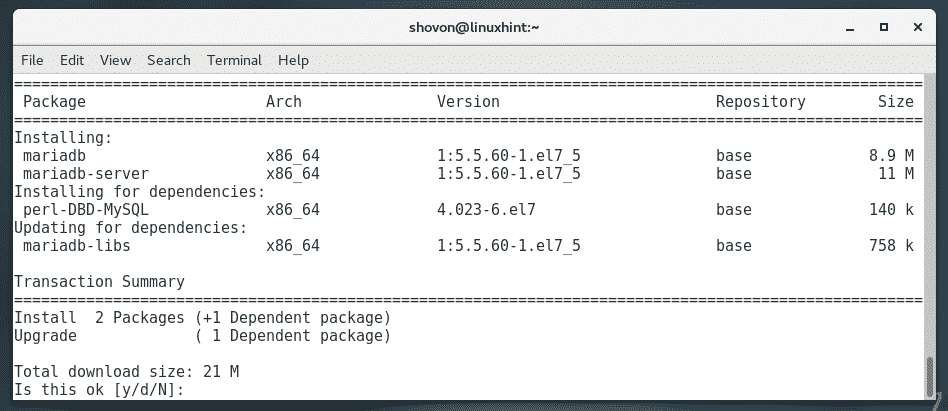
To install MariaDB on CentOS 7, run the following command:
Now, press y and then press <Enter>.
MariaDB database should be installed.
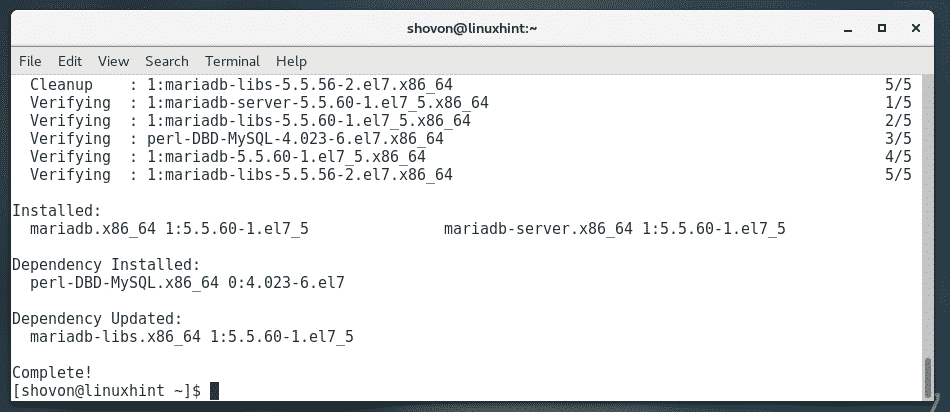
Now, start mariadb database service with the following command:

Also, add mariadb database service to the system startup with the following command:
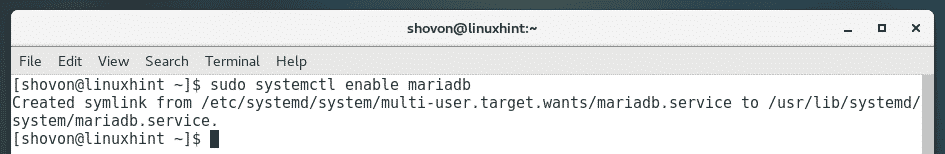
Creating a Database for Zabbix:
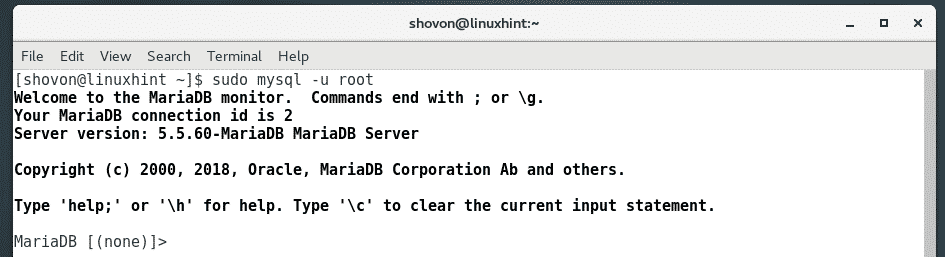
Now, you have to create a MariaDB database for Zabbix. To do that, run the following command:

NOTE: By default, no MariaDB root password is set. If you would like to set up a root password, then run mysql_secure_installation command and follow the interactive configuration wizard. Then connect to your MariaDB database with sudo mysql -u root -p command.
You should be logged into the MariaDB console.
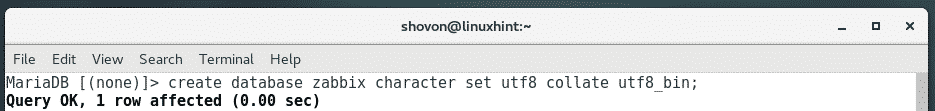
Now, create a MariaDB database zabbix with the following command:
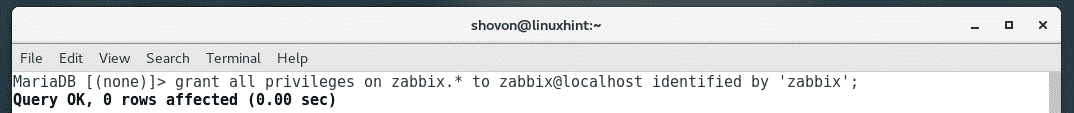
Now, grant all privileges to the database zabbix to the MariaDB user zabbix and also set the password for the user zabbix with the following command:
‘ZABBIX_DB_PASSWORD’;
NOTE: Repalce ZABBIX_DB_PASSWORD with the password that you want to set. In my article, I will set it to zabbix.
Now, exit out of the MariaDB console with the following command:
Now, run the following command to install the default Zabbix tables to the newly created database:

Now, type in the password for your MariaDB user zabbix and press <Enter>.
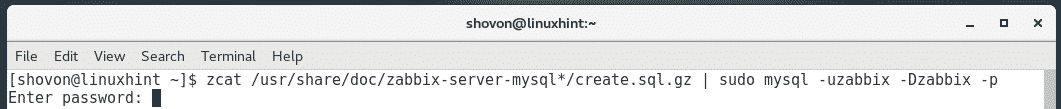
The default Zabbix tables should be installed.
Configuring Zabbix:
Now, you have to configure Zabbix.
First, open the /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.conf file with the following command:

Now, find the DBUser=zabbix line and put a new line DBPassword=zabbix below that as marked in the screenshot below.
NOTE: Replace zabbix with the password that you set for the MariaDB user zabbix.
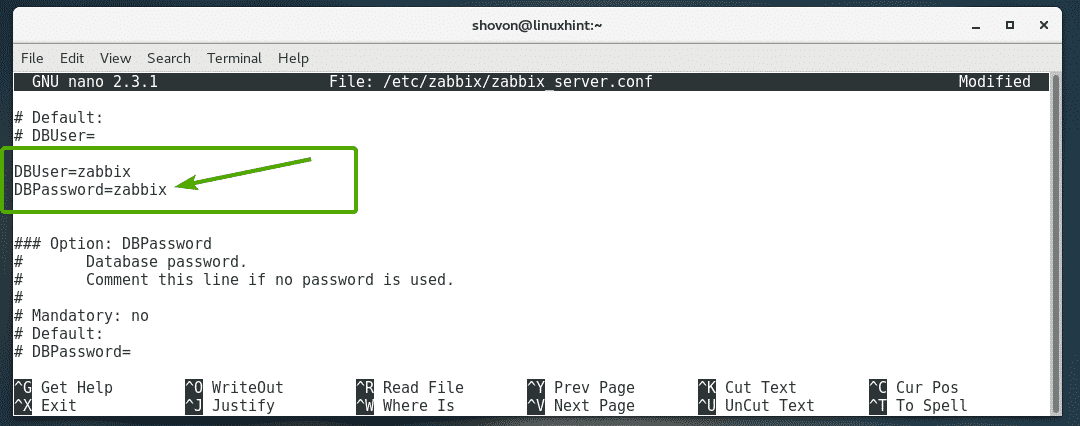
Once you’re done, save the file by pressing <Ctrl> + x followed by y and then press <Enter>.
Now, edit the /etc/httpd/conf.d/zabbix.conf file with the following command:

Now, you should see the following line as marked in the screenshot below.
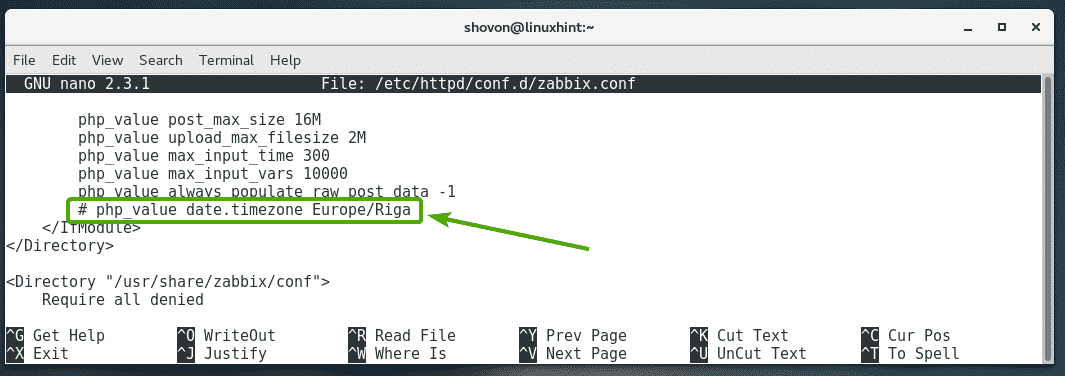
Uncomment the line (by removing the # sign from the beginning of the line) and change Europe/Riga to the time zone you want to set. You can find a list of time zone codes at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_tz_database_time_zones
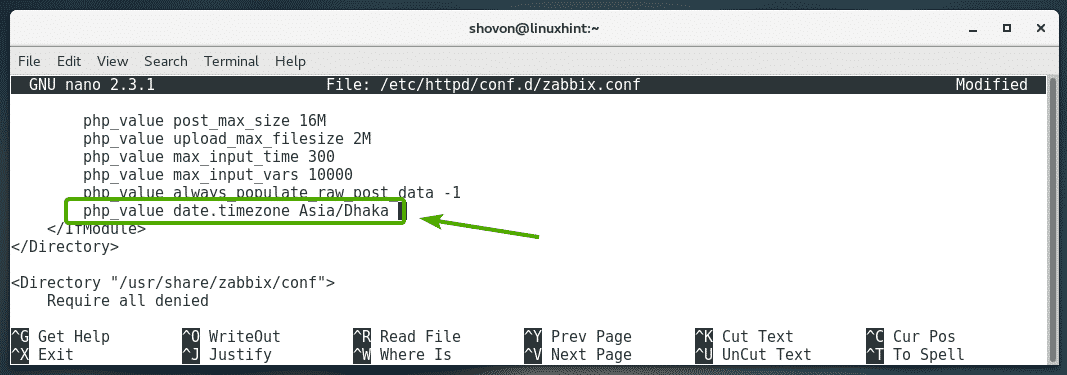
Once you’re done, save the file by pressing <Ctrl> + x followed by y and then press <Enter>.
Starting Zabbix Server:
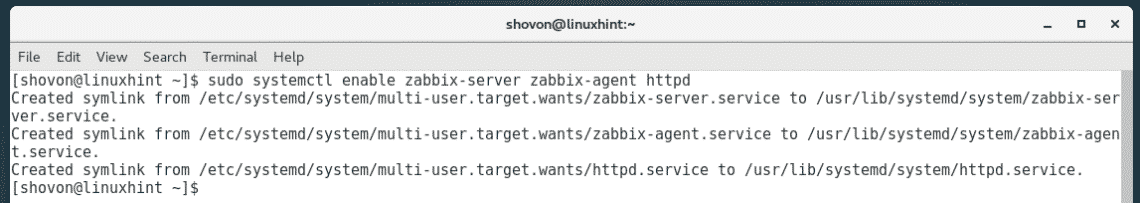
Now, you have to restart the zabbix-server, zabbix-agent, httpd services.
To do that, run the following command:

Now, add the zabbix-server, zabbix-agent, httpd services to the system startup with the following command:
Configuring Zabbix Frontend:
Now, you have to configure the Zabbix web frontend from a web browser.
You can access Zabbix frontend using the hostname or IP address of your CentOS 7 machine.
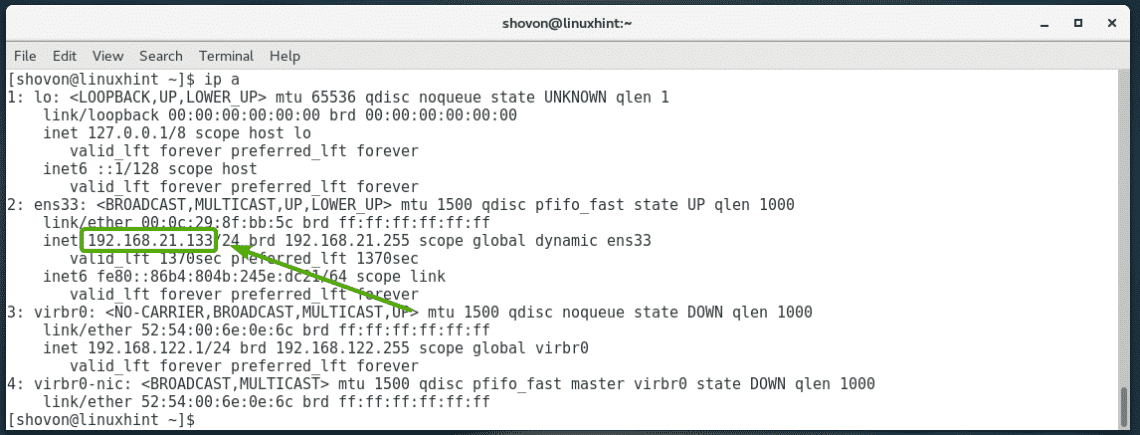
To find the IP address of your CentOS 7 machine, run the following command:
As you can see, the IP address is 192.168.21.133 in my case. It will be different for you. So, make sure to replace it with yours from now on.
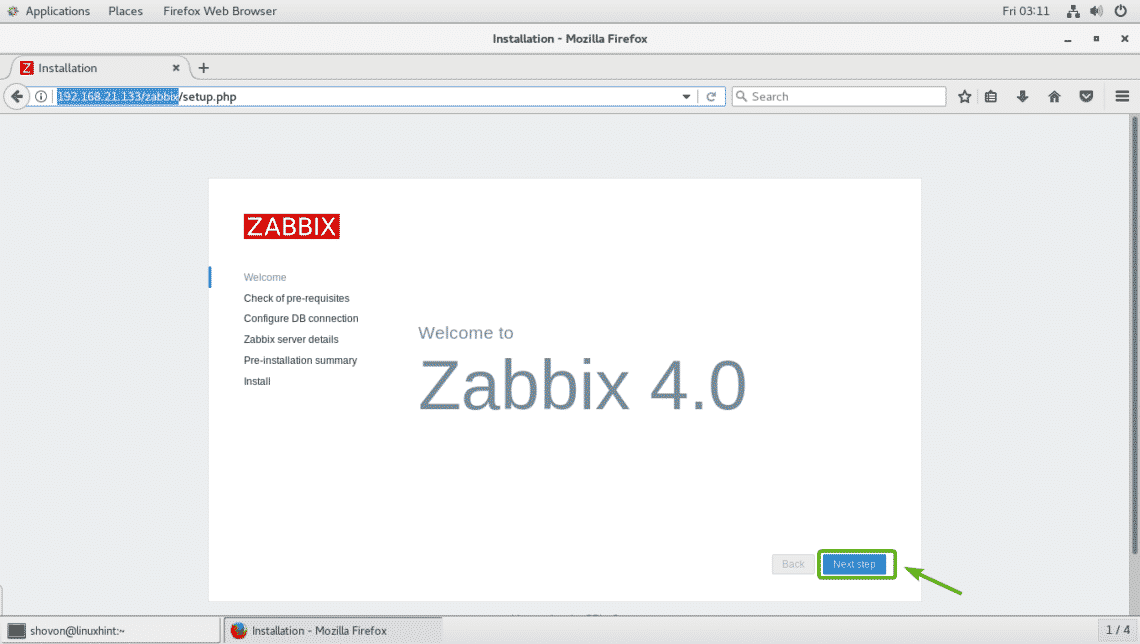
Now, visit the Zabbix frontend from your favorite web browser at http://192.168.21.133/zabbix. You should see the following page. Click on Next step.
Now, click on Next step.
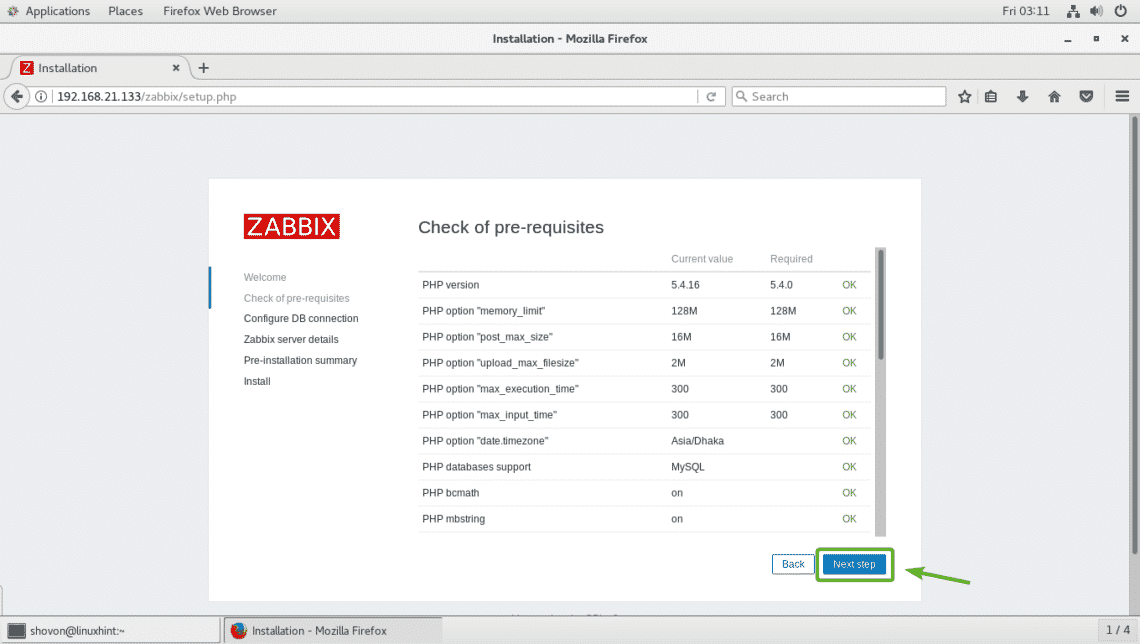
Now, type in the password that you set for your MariaDB user zabbix and click on Next step as marked in the screenshot below.
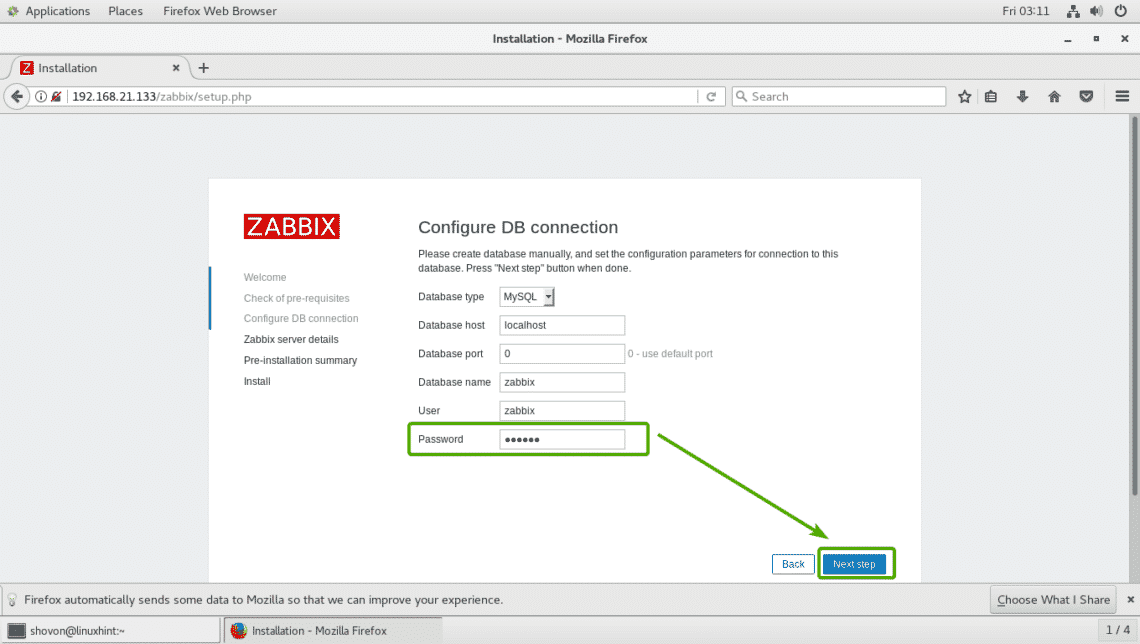
Now, click on Next step.
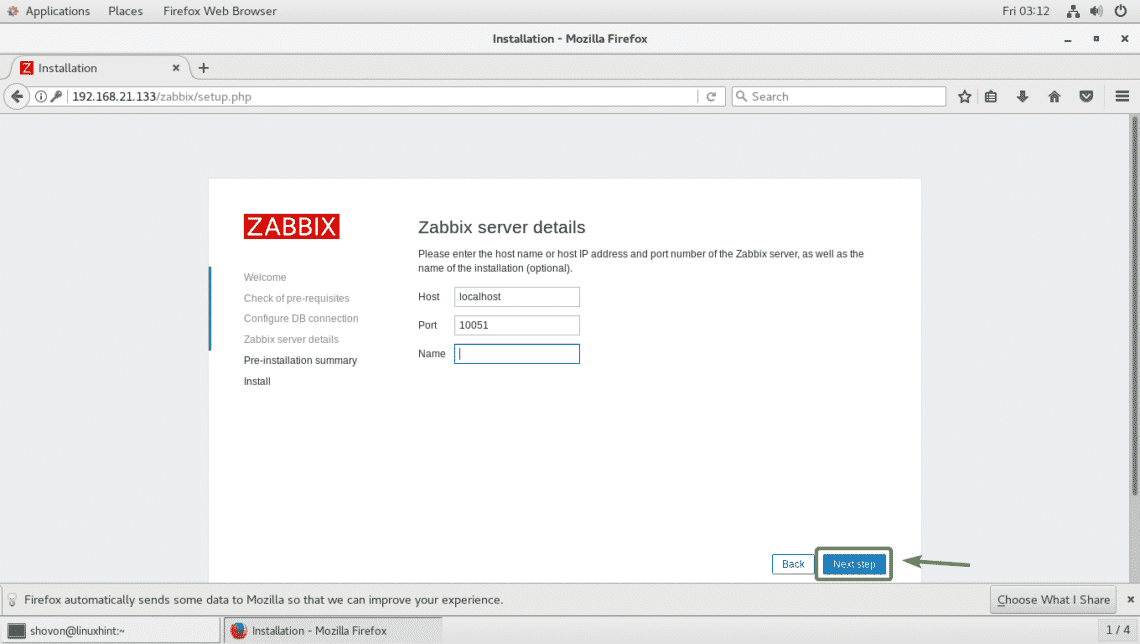
Now, check to make sure everything is alright. Then, click on Next step.
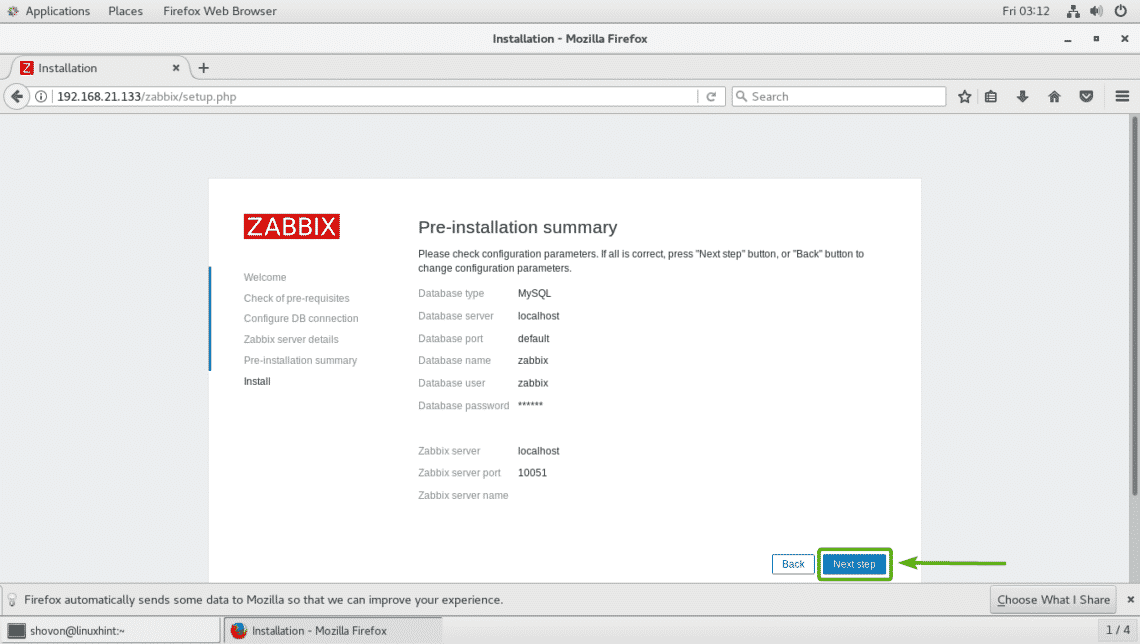
Zabbix frontend should be configured. Now, click on Finish.
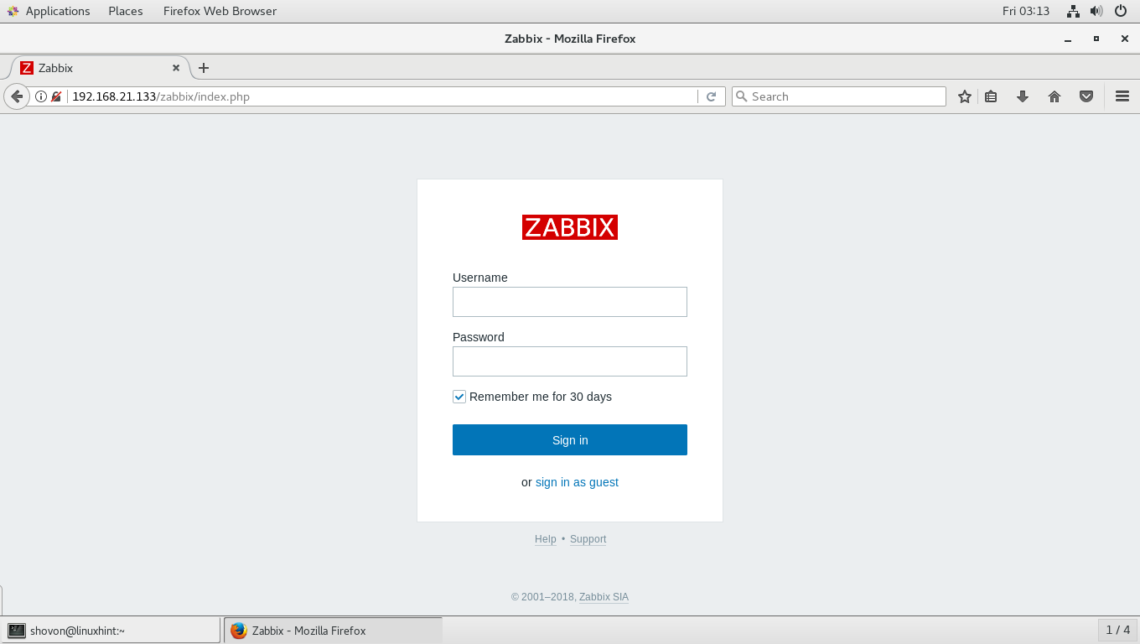
Now, you should be able to login to the Zabbix frontend. The default username is Admin and the default password is zabbix.
Once you log in, you should be able to see the Zabbix dashboard. You can configure Zabbix monitoring tasks from here.

So, that’s how you install Zabbix 4.0 on CentOS 7. Thanks for reading this article.


