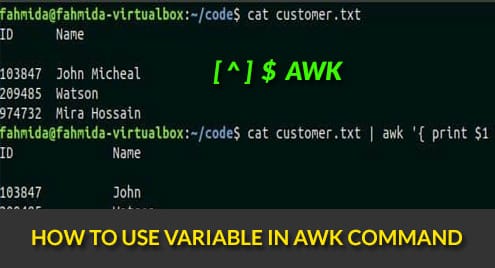
Example -1: Defining and printing variable
`awk` command uses ‘-v’ option to define the variable. In this example, the myvar variable is defined in the `awk` command to store the value, “AWK variable” that is printed later. Run the following command from the terminal to check the output.
Output:

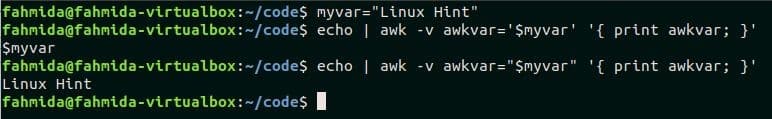
Example – 2: Using shell variable in awk with a single quote and double quote
The example shows how the shell variable can be used `awk` command. Here, a shell variable, myvar is declared with the value, “Linux Hint” in the first command. ‘$’ symbol is used with a shell variable name to read the value. The second command reads the variable, $myval with a single quote(‘) and the third command reads the variable $myvar with double quote(“) in the `awk` statement.
$ echo | awk -v awkvar=‘$myvar’ ‘{ print awkvar; }’
$ echo | awk -v awkvar="$myvar" ‘{ print awkvar; }’
Output:
It is shown in the output that the value of $myvar can’t be read when it is enclosed with a single quote (‘) and the output is $myvar. The value of $myvar is printed when it is enclosed with a double quote (“).
Example – 3: Reading ARGC variable in awk
ARGC variable is used to count the total number of command line arguments. Three command line arguments variables (t1, t2, t3) are passed in the following awk script. Here, the total number of arguments with the script is 4. Run the script from the terminal.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the script.

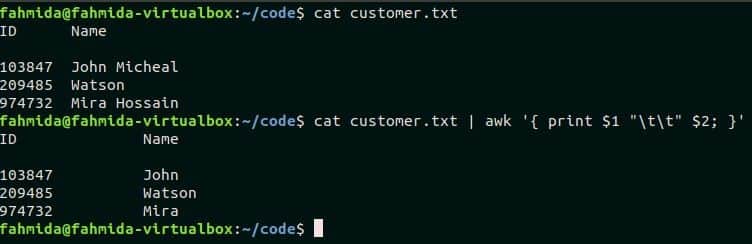
Example – 4: Reading file content by argument variables
Create a text file named customer.txt with the following content to practice this example. Here, every field of the file is separated by single tab space.
customer.txt
103847 John Micheal
209485 Watson
974732 Mira Hossain
Awk command can read each field from any text file by argument variables. There are two fields in customer.txt file. These are ID and Name. The following script will print these two fields by argument variables, $1 and $2 by separating two tab spaces. Run the script from the terminal.
$ cat customer.txt | awk ‘{ print $1 "tt" $2;}’
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands.
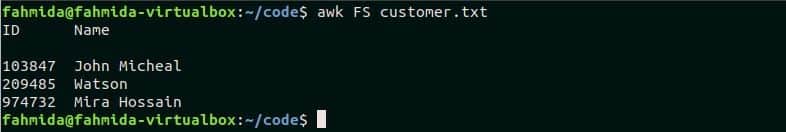
Example- 5: Using built-in variable, FS and field separator option with awk command
FS variable is used in awk command as a field separator. Space is used as a default value of FS. The following command will read the file customer.txt using space as field separator and print the file content. Run the command from the terminal.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the script.
Awk command can use other characters as field separator by using the ‘-F’ option. Create a text file named product.txt with the following content where ‘:’ is used as a field separator.
product.txt
102:Pencil:$5
103:Soap:$3
104:Shampoo:$10
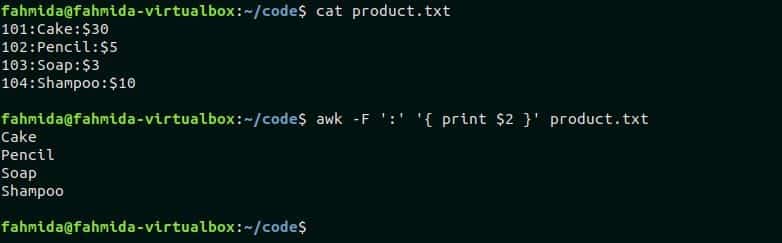
There are three fields in the file, product.txt that contains product id, name and price. The following awk command will print only the second field of each line. Run the commands from the terminal.
$ awk -F ‘:’ ‘{ print $2 }’ product.txt
Output:
Here, the first command printed the content of product.txt and the second command printed only the second field of the file.
Example – 6: Using built-in variable, NR with awk command
NR variable is used in awk command to count the total number of records or lines of a file. Create a text file named student.txt to test the function of this variable.
student.txt
John 20 3
Mira 22 1
Ella 18
Charle 15 8
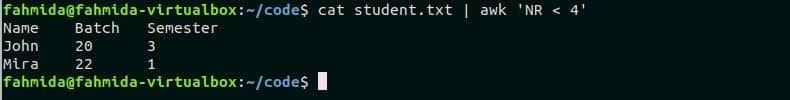
The following awk script will print the first three lines of product.txt file. Here, a condition is added by using the NR variable. The command will print those lines where the NR value is less than 4. Run the script from the terminal.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the script.
Example – 7: Using built-in variable, NF with awk command
NF variable is used in awk command to count the total number of fields in each line of a file. The following awk script is applied for the file, student.txt which is created in the previous example. The script will print those lines from student.txt file where the total fields are less than 3. Run the command from the terminal.
Output:
There is just one line exists in the file where the total number of fields is less than 3 that is printed as output.

Example – 8: Using built-in variable, OFS with awk command
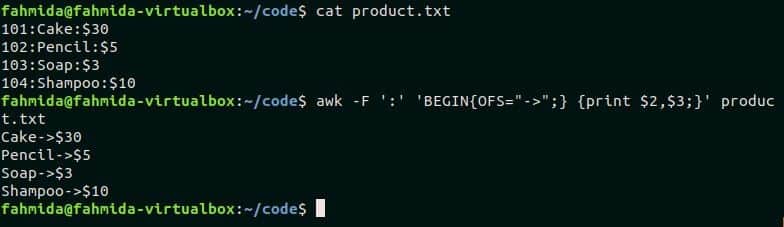
OFS variable is used in awk command to add output field separator in the output. product.txt file is used in this example to show the use of OFS variable. ‘:’ is used as field separator in product.txt file. The following awk script used ‘->’ as OFS value and, the second and the third fields of the file will print by adding this separator. Run the commands from the terminal.
$ awk -F ‘:’ ‘BEGIN{OFS="->";} {print $2,$3;}’ product.txt
Output:
The following output will print after running the commands.
Conclusion:
Most common uses of awk variables are tried to explain in this tutorial. Hope, the reader will be able to use awk variables properly in the script after practicing this tutorial.