Requirements
As stated above, JSON data type was introduced in MySQL 5.7.8; hence this or one of the newer Mysql versions should be installed in the system. Also, it’s preferred if it’s possible to use a GUI MySQL database management software instead of using console to manage the database, as it’s time consuming for a beginning to manage the database on console.
How to Install PHP My Admin
The following code snippet installs php my admin and configures it to access through any regular web browser. First command downloads the package list information, so they can be downloaded when issuing apt-get upgrade command. Second command install php my admin, second, third lines configures the php my admin to work with apache. Finally, the apache server is restarted to change to go into effect.
apt install phpmyadmin
sudo ln -s /etc/phpmyadmin/apache.conf /etc/apache2/conf-available/phpmyadmin.conf
sudo a2enconf phpmyadmin
sudo service apache2 reload
How to Install MySQL
The following code snippet installs mysql server, adds its port into UFW firewall’s exception list, starts it, and makes it automatically start when the computer system is turned on.
How to Create A Database with JSON Data Type
JSON data type is same as other default data types, except it has high flexibility, it allows to manage individual values in its key-value pair chain, acts as a data array; hence can retrieve the whole field with a single command, which is useful in caching the data in a large system.
This guide demonstrates the application of JSON data type with a database as following. The database contains two tables, and they are for brand and product. The brand table has “one to many” relationship with product table; hence one brand has many products, but one product is only belonged to one brand. The following SQL command creates a database named “graphics cards”, and a table named “category”.
Once the graphics card database, and brand table was created, insert two brand names into the name field of the brand table as following. The following command insert two brands named, AMD and Nvidia as brand names.
The next table can be created as seen in the following example. It has 4 columns (fields), id, name, brand_id, and attributes. brand_id field is the foreign key of brand table, attributes field is the JSON type field where attributes of the products are stored, for instance Nvidia GTX 1060 has various attributes like clock speed, memory clock, VRAM, model number, manufacturer name, supporting graphics API (direct3d, opengl) etc..
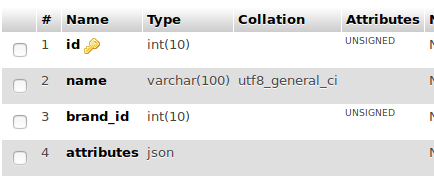
How to Insert Values into Database with JSON data type.
The following two commands insert two records into the database. The first record is for GTX 1030 product, and the second record is for GTX 1060 product. In both tables, as the attribute field a JSON formatted value contain. This value represents as an object array where the value is represented as key-value pair. Each key represents an attribute of the product. For instance, GTX 1030 product contains 384 CUDA cores, and in here it’s represented as an attribute. If it’s represented with the standard SQL way, the attribute field should be a table, and key (of key-value pair) attributes should be the fields in that table; hence an extra relationship is needed. On top of that, if one product contains extra attributes that other products don’t contain it might not be able to represent in the standard SQL way as the names of the fields are common for all the products. Here each product has its own distinct attributes.
name ,
brand_id ,
attributes
)
VALUES(
‘GTX 1030’ ,
‘1’ ,
‘{"CUDA Cores": "384", "Boost Clock": "1,468MHz", "Memory": "2GB", "Display Outputs":
{"DisplayPort": 1, "HDMI": 1}}’
);
INSERT INTO GraphicsCards.products(
name ,
brand_id ,
attributes
)
VALUES(
‘GTX 1060’ ,
‘1’ ,
‘{"CUDA Cores": "1280", "Graphics Clock": "1506", "Memory": "6GB", "Display Outputs":
{"DisplayPort": 1, "HDMI": 1, "DVI": 1}}’
How to Use JSON_OBJECT to Insert Values
The above records can be inserted into the database with JSON_OBJECT function. Unlike the standard JSON format, here it uses (key, value, key, value) format; hence it might be confusing for someone to identify what is key, and what is value of a long attribute list. However, in the database it still represents in standard JSON format.
How to Extract JSON Values from MySQL
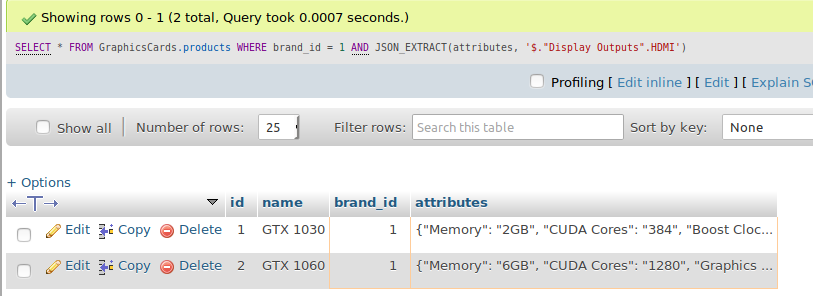
Extracting a value from JSON objects is quite simple as inserting a value. In here it uses JSON_EXTRACT() function for that purpose. JSON_EXTRACT() takes two arguments, the JSON object itself, and the key to be retrieved. The second argument takes its value as a key and the given subordinate keys, which is known as path expression in standard terminology. The following three commands represent how to retrieve values from a JSON object in 3 separate situations. The first one is when the key is one of the parent keys, the second command retrieves when the key has a space, the third command retrieves the 2nd child key of the parent key. The rule of thumb is when the JSON key has a space use double quotation enclosed in single quotation, when the key has no space just use the single quotation. Either way when retrieving the child keys, it’s important to express the path as binary tree way, which means first the parent key, then its one of the child keys, then its one of the child keys.
Key When It Has No Space
Key When It Has A Space
Key When It Has One Subordinate Key
Conclusion
Relational databases are actually quite versatile in their data types and functions so you may have been to be surprised what a SQL DB can do with JSON.