Syntax:
The syntax for four types of conditional statements is mentioned below.
- if statement
statement
}
The statement executes when the if condition returns true.
- if-else statement
statement-1
}
else{
statement-2
}
The statement-1 executes when the if condition is true and the statement-2 executes when if return false.
- if-elseif statement
statement-1
}
elseif{
statement-2
}
elseif{
statement-3
}
…….
else{
statement-n
}
This conditional statement is used for executing a statement based on multiple if condition. If the first condition is false then it checks the second condition. If the second condition is false then it checks the third condition and so on. If all conditions return false then it will execute the statement of else part.
- Ternary (?:) operator
Ternary operator can be used as an alternative of if-else statement. If the condition true the statement-1 will execute and if the condition false then statement-2 will execute.
Example-1: Using simple if in awk
Create a text file named emplyee.txt with the following content. Suppose, you have to find out the department name, age, and salary of the employee whose id is 11002.
employee.txt
11002 HR 32 $1500
11003 Marketing 26 $1200
11004 HR 25 $2500
A simple if condition is used in the following script to search the id 11002 in the first field of the file. If the condition becomes true then it will print the values of the other fields of the corresponding line otherwise nothing will be printed.
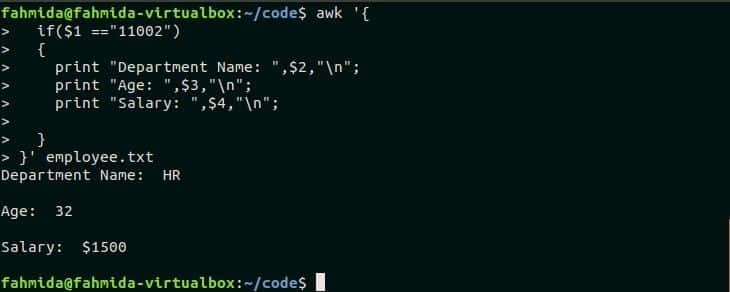
if($1 =="11002")
{
print "Department Name: ",$2,"n";
print "Age: ",$3,"n";
print "Salary: ",$4,"n";
}
}’ employee.txt
Output:
The id, 1102 exists in the file. So, it printed the other values of the employee.
Example-2: Using if-else in awk
Suppose, you want to print the salary information of the employees whose age is less than or equal to 40 and print the age information for other employees. The following awk script can do this task. There is only one employee in employee.txt file whose age is more than 40 and all other employee’s age is less than 40.
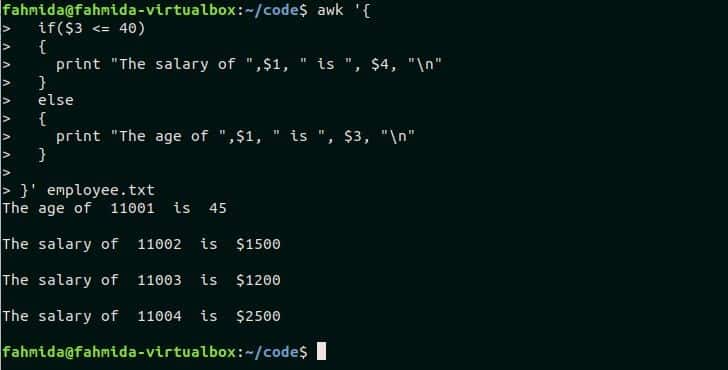
if($3 <= 40)
{
print "The salary of ",$1, " is ", $4, "n"
}
else
{
print "The age of ",$1, " is ", $3, "n"
}
}’ employee.txt
Output:
The following output will appear after running the script.
Example-3: Using if-elseif in awk script
Create a text file named person.txt with the following content.
person.txt
MARTIN Male Service Holder
LILY Female Manager
ROBINSON Male CEO
Create a awk file named if_elseif.awk with the following code to print the favorite color of each person whose name exists in the file. If-elseif statement is used in the script to do this task. The script will read the first field value of the file, employee.txt and check with a particular value. If the first if condition becomes false then it will check the second if condition and so on. When any if condition becomes true then a color value will be assigned. If all conditions become false then None will be assigned as the color value. The favorite color of each person will print or “No person found” will print if no person name matches.
if_elseif.awk
name=$1;
if ( name=="JACKSON" ) color="Blue";
else if (name=="MARTIN") color="Black";
else if (name=="LILY") color="Red";
else if (name=="ROBINSON") color="White";
else color="None";
if(color!="None") print "The favorite color of ", name, "is ", color;
else print "No person found";
}
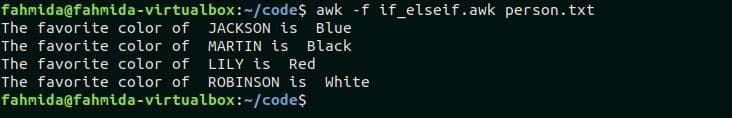
Run the following command to execute the file if_elseif.awk with person.txt
Output:
The following output will appear after running the command.
Example-4: Using ternary operator in awk
The third field of person.txt file contains the profession of each person. The following ternary operator reads each line of the file and matches the third field value with “Manager”. If the value matches then it will print the name of the person and otherwise it will print the gender of the person.
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the script. One person with “Manager profession exists in the person.txt. So, the name of one person is printed and gender is printed for other persons.

Example-5: Using multiple conditions in if statement
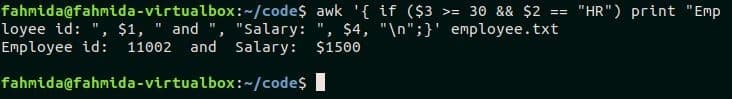
Logical OR and Logical AND can be used to define multiple conditions in the conditional statement of awk script. The following awk script reads each line of employee.txt and checks the age and designation with particular values. Logical AND is used in the if condition. When the age value is greater than or equal to 30 and designation is “HR” then the corresponding employee id and salary will print.
$1, " and ", "Salary: ", $4, "n";}’ employee.txt
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the script. There is only one employee exists with the designation, “HR” in employee.txt. Id and salary information for this employee is printed here.
Conclusion:
Most common uses of the conditional statement of any standard programming are supported by awk command. How you can use single and multiple conditions in awk is explained by using very simple examples here. Hope after practicing these examples the learner will be able to use conditional statement properly in awk script.