In this lesson, we will setup the Jupyter Notebook server on a Ubuntu machine and also connect to the Jupyter server as well with which we will be able to make new Jupyter Notebooks and run some sample Python code as well.
Getting Started
We will start by installing most basic components for this lesson which are Python and PIP. Let’s start with basic updates in our machine:
Here is what we get back with this command:
Next, we can install required components in a single command:
This installation might take some time to install depending on network speed as many dependencies are being installed here. We are using Python 2.7 with PIP package manager with which we can use and install many other python modules as we go. Finally, many of Jupyter’s dependencies work on Python-C extension, so we installed the python-dev dependency as well. To verify that everything went well, let us check the Python & PIP version with these commands:
pip –version
We will get back:
Installing IPython & Juptyr
We can move on to installing most important parts of this lesson. Let us run the following commands to install IPython & Juptyr on our machine:
sudo -H pip install jupyter
Again, even this command can take more time to complete depending on network speed. Once this command is complete running, we can finally start the jupyter notebook as:
You can start Jupyter as a non-root user as well. If you start Jupyter as a root user, we will have to use the –allow-root flag. Once this starts, the terminal will look like this:
Accessing Jupyter Console
We can access the Jupyter server from the URL shown in the console. If you’re running this server on a remote server, we will have to tunnel into the IP through SSH. We can do this with this command:
Once you execute this command, you can again SSH into your server and execute the command to start Jupyter notebook with this command:
Accessing Jupyter Notebook
Once you’ve started the Jupyter notebook server through SSH, you will see a URL like this in the terminal window:
Take note of one of the tokens in the URL. Now, open the following URL in your local machine browser:
You will see something like:
Once you’re in this screen, we can input the token we collected in previous step in the provided field. We will be inside once we hit Enter. We will see a screen like this:
We can now create a new notebook:
We can provide a name to this notebook by clicking on title bar:
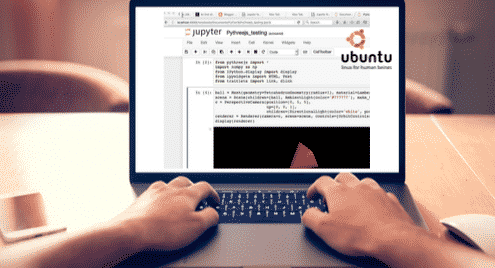
Finally, you can write sample Python code and execute in the browser itself:
Conclusion
In this lesson, we looked at how we can install and start using Jupyter notebook server on Ubuntu 18.04 machine.