History settings:
Many variables are used to control the command history records. Bash stores command history in two ways. It can be stored in a file and in memory. HOSTFILE variable is used to set the location and name of the history file. By default, history information stored in .bash_history file. How many commands can be stored in a file is set by using HISTFILESIZE variable and how many commands of the current session can be stored in the memory is set by HISTSIZE variable. Open the .bashrc file in any editor and find out the default settings of these parameters. Here, text editor is used to edit this file.

According to the content of this file, the default value of HISTFILESIZE is 2000 and HISTSIZE is 1000. You can change these values according to your choice.

Enable/Disable History Overwriting Option:
For each new session, the history file is overwritten by the current history commands at the end of the session. If you want to keep the previous history command and want to add the new history records at the end of the file then execute the following command.
Run the following command to check the current setting of history overwriting option.
Run the following command to overwrite the history file.

Display the list of previously executed bash commands:
To retrieve the list of currently executed commands of the current session run the following basic command.

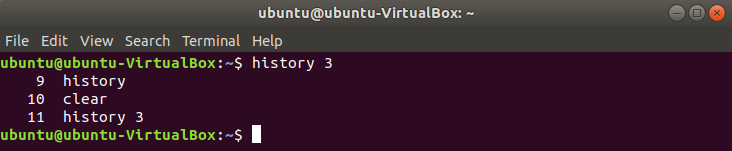
You can retrieve the particular number of history by mentioning the number with history command. The following command retrieves 3 lastly executed commands from the history.
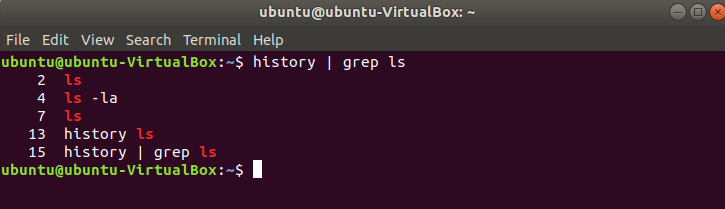
The history list of the particular command can be retrieved by using the command with history command. For example, the following command retrieves the history list of all ‘ls’ command.
Executing command from the history:
You can easily execute any command from the history by mentioning the line number with ‘!’ symbol. The following command will execute the command of line number 17 from the history file and clear the screen.

You can use negative position value to execute commands from the history. In the following example, three commands are executed and the first executed command is executed from the history by using a negative value.

You can use ‘!!’ symbol to execute the most recent command from the history. In the following example, ‘ls’ command is executed last. So, when ‘!!’ is executed then it executed the ‘ls’ command again.

Display the history list by date and time:
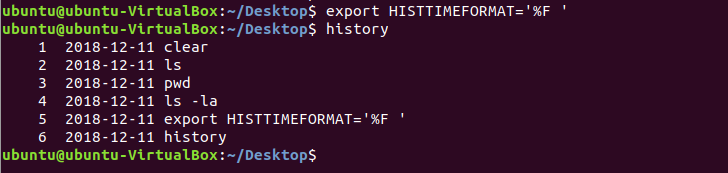
HISTTIMEFORMAT variable is used to retrieve command history information by date and time. ‘%F’ is used retrieving date ‘%T’ is used for retrieving time. Run the following command to retrieve history list by date.
Remove duplicate commands from the history:
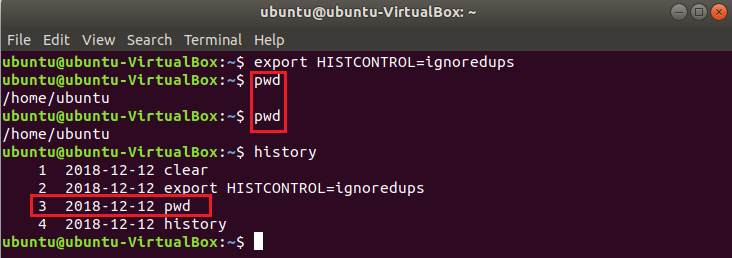
The command history list may contain the entry of many duplicate commands if the user runs the same command multiple times. If you want to omit the duplicate command from the history at the time of retrieving the list then you have to use HISTCONTROL variable with value ‘ignoredrups’.
Filter any command from the history:
You can use HISTIGNORE variable to filter any command from the history when retrieving the executed command list. If you want to omit the ‘date’ command from the list then run the following command.

Unset export command:
You can unset export command for any defined variable types. For example, if you want to unset HISTIGNORE variable which is assigned to ignore ‘date’ command then run the following command.

Disable History of command:
When you don’t want to keep the records of the executed commands for any security purpose then you will need to disable the history command. If the value of HISTSIZE variable is set to 0 then no executed command of the current session will be stored in the memory or in the history file. Open .bashrc file and set the value of HISTSIZE to 0.

Run the following command to create the effect of the change of the .bashrc file. Run some commands to check history command is disabled or not.

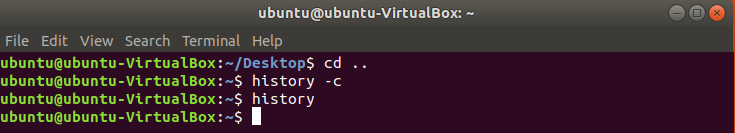
Clear History of commands:
History of commands can be cleared or deleted by using history command with –c option. You can use this option when you want to remove the records of executed command without disabling the history command.
Scrolling History list:
You can move through the previously executed commands easily by using up arrow and down arrow. Without using arrow key you can go backward to the history list by pressing Ctrl+P and can go forward to the history list by pressing Ctrl+n. Enable the history command, run some commands and check these options.
Searching command from history:
You can search command from the history by pressing Ctrl+R. When these keys are pressed then a search option will appear. The command will search from the history based on the keypress by the user.

Conclusion
The Linux users can save their times by using history command efficiently. Most commonly used history commands are tried to explain in this tutorial for helping the users to use this command properly.




