Syntax:
date [option] [MMDDhhmm [ [CC] YY] [.ss] ]
Different format codes or characters can be used with the date options to generate the formatted output. Some common options and format types are mentioned below.
Options:
| -d or –date=String | It displays the time set by the String value. |
| -s, –set=String | It sets the time set by the String value. |
| -f or –file=DateFile | It is used to process multiple dates. |
| -I or –iso-8601[=Timespec] | It is used to create an ISO 8601 compliant date/time string output. |
| -r or –reference=File | It is used to display the last modification time of a file. |
| -u, –utc, –universal | It is used to display or set Coordinated Universal Time. |
| –help | It is used for getting the help of this command. |
| –version | It is used to get version information. |
Some Format codes:
| %a | Print weekday names in short form (e.g., Sun) |
| %A | Print full weekday names (e.g., Sunday) |
| %b | Print month name in short form (e.g., Jan) |
| %B | Print full month name (e.g., January) |
| %c | Print date and time (e.g., Mon Mar 11 23:05:25 2019) |
| %C | Print century; like %Y, except omit last two digits (e.g., 25) |
| %d | Print day of the month (e.g, 01) |
| %Y | Print 4 digits year (e.g. 2019) |
| %y | Print 2 digits year (e.g. 19) |
| %D | Print date; same as %m/%d/%y |
| %e | Print day of the month, same as, %d |
| %F | Print full date; same as, %Y-%m-%d |
Example-1: Display date in the particular format
By default `date` displays the current date and time value. Each part of date and time values can be printed separately by using different data options. The following command will print the date value only.
Output:
Here, ‘%d’ is used for printing day value, ‘%B’ is used for printing full month name and ‘%Y’ is used for printing full year value.

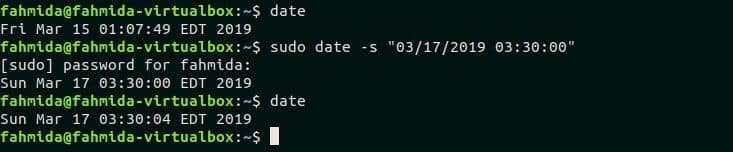
Example-2: Change the current date and time
The current date and time value can be changed by using -s option. You must have root privilege to change the system’s date and time. The following command will change the current date to ‘03/17/2019’ and time to ‘03:30:00‘.
$ sudo date -s "03/17/2019 03:30:00"
$ date
Output:
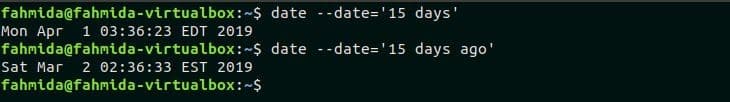
Example-3: Find the particular date and time using days
Sometimes we need to find out the future or previous date and time. Any date can find out by using `date` command and defining days, month and year values in –date option. The following commands will calculate the date and time after 15 days and before 15 days.
$ date –date=’15 days ago’
Output:
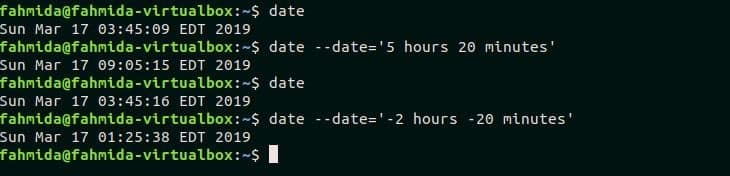
Example-4: Find the particular date and time using times
Like the previous example, future or previous times can be calculated by using `date` command. The following commands will calculate the future time after ‘5 hours 20 minutes’ of current times and before 2 hours and 20 minutes of current times.
$ date –date=‘5 hours 20 minutes’
$ date
$ date –date=‘-2 hours -20 minutes’
Output:
Example-5: Convert current date and time to UNIX epoch time
According to UNIX epoch time, the time value is calculated in seconds from the date, 1st January 1971. This time value can be used to calculate the time difference. `date` command can be used to convert any date value to UNIX epoch time. The following command will convert the current system date and time to UNIX epoch time.
Output:

Example-6: Convert UNIX epoch time to date and time
Using `date` command anyone can convert any UNIX epoch time to date and time value. The following command converts ‘1552298500′ epoch value to its corresponding date and time value.
Output:

Example-7: Find out the weekday based on date
`date` command can be used to find out the weekday name, month name or year value from any date value. The following command will find the weekday name of 1st January 2019 and the output is ‘Tuesday’.
Output:

Example-8: Using date command in a bash script
A bash file named timediff.sh is created with the following code. In this script, two date values are taken from command line arguments which are stored on $1 and $2. $START variable stored the UNIX epoch time value of $1 and $END variable stored the UNIX epoch time value of $2. The difference between these two values is calculated and stored to $diff variable in seconds. Next, the seconds are converted to days and printed.
timediff.sh
START=`date -d $1 +%s`
END=`date -d $2 +%s`
((diff=$END–$START))
((days=$diff/(60*60*24)))
echo "The time escaped = $days days"
The script is executed with two date values as command line arguments. Here, 2019-01-01 and 2020-01-01 dates are used and the difference between these two dates is 365 days.

Conclusion
You can use `date` command for various purposes in the bash script. Some uses of date values are explained in this tutorial with the above examples. You can also use this command to separate the parts of time value by using different options and formats. Hope, this tutorial will help the readers to understand the use of `date` command and apply them properly.