Working with OS module
To start working with the OS module and make scripts use this module, we will use the same import statement in all the scripts we write:
This statement imports and brings required OS module dependencies into our scope.
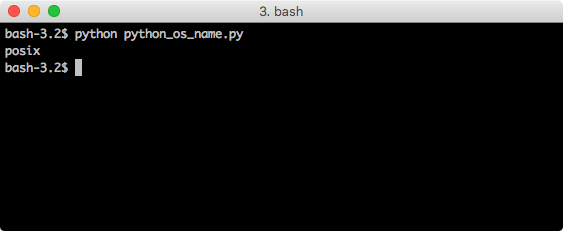
os.name
This is the most basic operation we can perform with this module. This is self-descriptive in nature that this function will give the OS we are using right now:
print(os.name)
When we run this program, we will see this output:
Of course, this script will give different output based on the host platforms.
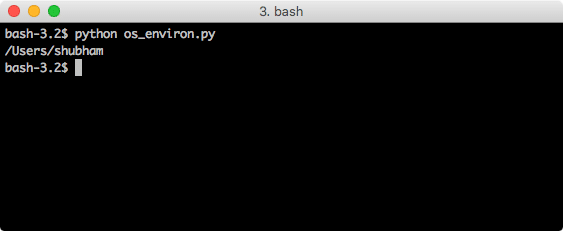
os.environ
Using the environ process parameter, we can get data about the environment variables defined in the system. Let’s put this to use here:
home_env = os.environ[‘HOME’]
print(home_env)
When we run this program, we will see this output:
Again, this script will give different output based on the configured params.
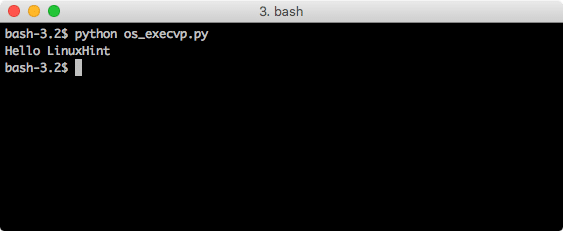
os.execvp
Using OS module, we can even execute other scripts present on the machine. For this, let’s define a sample script here, with name ‘sample.py’ and with following contents:
In the program, let’s execute this script using the python interpreter:
interpreter = "python"
script = ["hello.py"]
print(os.execvp(interpreter, (interpreter,) + tuple(script)))
When we run this program, we will see this output:
This is actually a very important command with which we can write scripts which run other scripts as well on the basis of the flows and conditions.
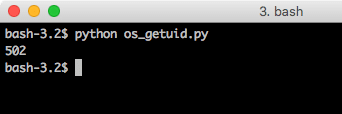
os.getuid
Using the getuid function, we can obtain the currents process ID (or PID). With this, we can control process as well. Let’s put this function to use:
print(os.getuid())
When we run this program, we will see this output:
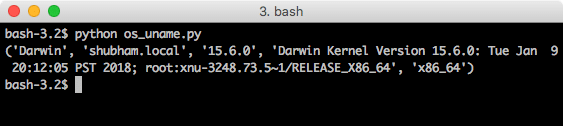
os.uname
Using the uname function, we can identify the current OS in detail. Let’s put this function to use:
print(os.uname())
When we run this program, we will see this output:
This is quite the information regarding the platform.
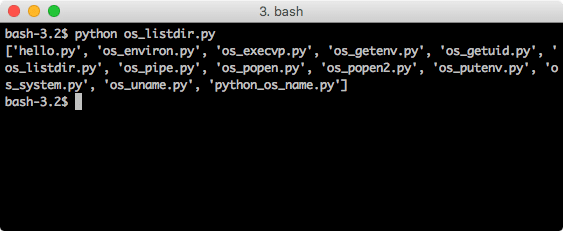
os.listdir
Many times in our scripts, we can even obtain all available directories in current path of execution to perform any number of operations on them. We will only list available directories in a script here:
print(os.listdir("."))
We provided a . here so that the script prints directories and files present in current directory. When we run this program, we will see this output:
os.system
Using os system function, we can run a command in the Python script, which will act as if we were running it directly from the command line. For example:
files = os.system("users > users.txt")
When we run this program, we will see this output:
In this lesson, we read about various functions provided by the Python OS module. See more lessons on Python here.